
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Bifidobacteria
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 06.07.2025
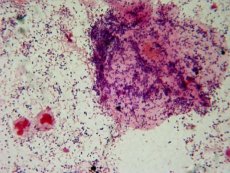
Bifidobacteria are gram-positive, non-spore-forming, non-motile rods. Pleomorphic, diphtheroid or club-shaped with one rounded end and the other cone-shaped, less intensely stained. Cells can be coccoid, elongated, bifurcated and even branched; they are located singly, in pairs, in the form of the letters V and Y, in short chains or in groups in the form of Chinese characters. The type species is Propionibacterium.
Read also: Top 10 Foods Containing Probiotics
Cultural properties of bifidobacteria
Most bacterial strains grow most rapidly under anaerobic conditions, in special media, with an optimum pH of 7.0 at 25-45 °C.
 [ 8 ], [ 9 ], [ 10 ], [ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ]
[ 8 ], [ 9 ], [ 10 ], [ 11 ], [ 12 ], [ 13 ]
Biochemical activity of bifidobacteria
Bifidobacteria have a fermentative metabolism. Fermentation products include combinations of propionic and acetic acids. Most strains form ammonia from protein substances.
 [ 14 ], [ 15 ], [ 16 ], [ 17 ], [ 18 ]
[ 14 ], [ 15 ], [ 16 ], [ 17 ], [ 18 ]
Ecological niche of bifidobacteria
Human skin, human and animal digestive tract: found in dairy products.
 [ 19 ], [ 20 ], [ 21 ], [ 22 ], [ 23 ], [ 24 ]
[ 19 ], [ 20 ], [ 21 ], [ 22 ], [ 23 ], [ 24 ]
Antimicrobial susceptibility
Bifidobacteria are sensitive to the action of commonly used antiseptics and disinfectants.

