
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
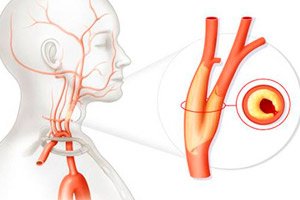
Among the numerous vascular diseases, atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is quite common. This is a chronic pathology accompanied by a disorder of cholesterol metabolism and capable of entailing life-threatening complications. The development of the disease is slow, progressive, and often asymptomatic. The most common complication is ischemic stroke.
Epidemiology
Without affecting the possible causes of carotid atherosclerosis, in the presence of a tendency to the disease, a gradual deposition of cholesterol deposits occurs on the internal vascular walls. Clinical signs of damage appear when the arterial vessel narrows by more than 50%: this is when patients begin to seek medical attention.
Atherosclerotic deposits most often fill the cervical segment of the carotid artery and are of small length. The severity of the pathological process is judged by the degree of narrowing of the vascular lumen relative to the normal segment of the vessel located behind the affected area.
Numerous studies by scientists have shown that with stenosis of the internal carotid artery exceeding 70% of the lumen, the risk of ischemic stroke increases 5 times. Blood supply to the brain occurs mainly from a pair of internal carotid arteries and a pair of vertebral arteries. With arterial stenosis exceeding 70% of the lumen, the basic parameters of blood flow are disrupted, which leads to the formation of microthrombi, damage to the internal vascular wall, instability of atherosclerotic deposits and their detachment. Moving along the vessel, pathological elements get stuck in it, which leads to ischemia of the corresponding area of the brain and to its irreparable damage. [ 1 ]
Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is one of the pathologies included in the structure of cerebrovascular disease, which in many cases ends in death. The pathology has a prevalence of 6 thousand cases per hundred thousand of the population. The predominant age of patients is from 55 years.
Most often the disease affects:
- the bifurcation zone where the carotid artery branches into internal and external;
- the orifice of the internal carotid artery (the part closest to the branching point);
- orifice of the vertebral arteries;
- siphon of the internal carotid artery (the bending area at the entrance to the cranium).
This localization is due to the fact that in these areas there is flow turbulence, which increases the likelihood of damage to the inner wall of the vessels.
Causes atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries
Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries can develop under the influence of many reasons, for example:
- disruption of fat metabolism, increased levels of total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins, decreased levels of high-density lipoproteins;
- systematic increase in blood pressure, hypertension;
- diabetes mellitus, long-term high blood glucose levels;
- overweight, physical inactivity;
- smoking, other bad habits;
- poor nutrition, excessive consumption of animal fats against the background of a shortage of plant products, abuse of fast food and low-quality semi-finished products;
- regular stress, etc.
It is important to note that all the causes of carotid artery atherosclerosis are still unknown and continue to be studied. Scientists name prolonged hyperlipidemia as the underlying cause, which leads to the accumulation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of arterial vessels. Additionally, there is a parietal deposition of connective tissue threads and calcium salts. The plaques gradually increase, change shape, blocking the blood lumen.
Genetic predisposition plays a major role in the initial increase in the content of “bad” cholesterol and triglycerides, and in general the situation worsens with the appearance of chronic diseases that aggravate mineral-fat metabolism disorders. [ 2 ] Such chronic pathologies include:
- Hypertension, prolonged use of medications that lower blood pressure (antihypertensive drugs negatively affect the course of lipid processes).
- Diabetes mellitus (especially the insulin-dependent type) leads to the early development of atherosclerosis, which is caused by disturbances in fat metabolism, an increase in the content of atherogenic lipoproteins in the blood, and increased production of collagen with its subsequent deposition on the vascular walls.
- Thyroid pathologies and hypothyroidism are accompanied by severe cholesterolemia against the background of normal levels of β-lipoproteins.
- Gouty arthritis is almost always accompanied by hyperlipidemia, a disorder of mineral-fat metabolism.
- Infectious and inflammatory processes, such as herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus, often cause background lipid metabolism disorders (in approximately 65% of cases).
Risk factors
Factors that have an indirect influence on the development of carotid artery atherosclerosis can be divided into the following categories:
- Permanent factors that cannot be eliminated.
- Transient factors that can be eliminated.
- Potentially transient factors that can be partially eliminated.
The first category of constant factors includes the following:
- Age, because the risk of atherosclerotic changes increases significantly with age. Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is especially often found in patients over 45 years of age.
- Male gender, as men are prone to an earlier onset of atherosclerosis. In addition, the disease is much more common in men, which may be due to a higher percentage of harmful male habits, a greater tendency to eat fatty foods.
- Unfavorable heredity, because atherosclerosis is often “passed on” through family lines. If parents have been diagnosed with carotid artery atherosclerosis, then children have an increased risk of developing the disease early (before age 50). [ 3 ], [ 4 ]
The second category of transient factors includes those that each person can eliminate independently by changing their lifestyle:
- Smoking, which is accompanied by an extremely negative effect of tar and nicotine on the vascular walls. This applies to both heavy smokers and passive smokers who inhale cigarette smoke for many years and do not smoke themselves.
- Poor nutrition, associated with the predominant consumption of animal fats and foods with a high cholesterol content.
- A sedentary lifestyle, which contributes to the disruption of lipid metabolism and the emergence of other causal pathologies (obesity, diabetes, etc.).
The third category includes factors that can be partially eliminated - for example, treating existing diseases, establishing control over them to prevent relapses. Provoking diseases can be:
- Hypertension, which leads to increased permeability of the vessel wall, the formation of a blocking plaque, and deterioration of the elasticity of the carotid arteries.
- A lipid metabolism disorder characterized by high levels of cholesterol and triglycerides.
- Diabetes and obesity, accompanied by the same lipid metabolism disorder.
- Toxic and infectious effects that damage the inner walls of blood vessels, which contributes to the deposition of atherosclerotic plaques on them.
It is very important to know the main factors that can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries. This is necessary, first of all, to understand the basics of disease prevention, slowing down and easing its course. [ 5 ], [ 6 ]
Pathogenesis
The term "atherosclerosis" is a combination of two words: athero (porridge) and sclerosis (hard). As the pathology develops, cholesterol, products of cellular decomposition, calcium salts and other components are deposited inside the vessels. The disease develops slowly, but steadily progresses, which is especially noticeable in patients with high cholesterol in the blood, high blood pressure, diabetes, etc. The impact of any damaging factor on the vessel wall entails a local inflammatory reaction. Lymphocytes enter the damaged area through the circulatory system, inflammation begins. This is how the body tries to cope with the damage. Gradually, new tissue is formed in this area, the ability of which is to attract cholesterol present in the bloodstream. When cholesterol settles on the vascular wall, it oxidizes. Lymphocytes capture oxidized cholesterol and die, releasing substances that contribute to a new cycle of inflammation. Alternating pathological processes provoke the formation and growth of atherosclerotic growths, gradually blocking the vascular lumen. [ 7 ]
Triglycerides, cholesterol and lipoproteins are involved in the pathogenesis of coronary heart disease, especially atherosclerosis. [ 8 ], [ 9 ] It has been shown that decreased concentrations of high-density lipoproteins (HDL) and increased triglycerides are responsible for the genesis of atherosclerotic lesions. [ 10 ] In the recommendations of the National Cholesterol Education Program, an HDL level below 1 mmol / L is considered the threshold value below which patients are considered at risk of developing coronary heart disease.
The carotid arteries are the most important vessels in the human body. All head structures are fed through these arteries, including the brain, which consumes at least 1/5 of the total volume of oxygen entering the bloodstream. If the lumen of the carotid arteries narrows, this is inevitable and has an extremely negative effect on brain function.
Normally, a healthy vessel has a smooth inner wall, without any damage or additional inclusions. When cholesterol plaques are deposited, they indicate the development of atherosclerosis: the composition of plaques is usually represented by calcium-fat deposits. As the size of pathological formations increases, blood flow in the carotid arteries is disrupted.
As a rule, atherosclerotic changes in the carotid arteries are not primary and appear following damage to other arterial vessels. The early stages of the disease are not stenotic in nature and do not lead to narrowing of the vascular lumen. However, as the disease progresses, the situation worsens, cerebral trophism is disrupted, which may further be complicated by ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
The carotid arteries must work constantly, because the brain always needs oxygen and nutrients. However, under the influence of many reasons, atherosclerosis is formed, blood flow worsens, and brain nutritional deficiency occurs. [ 11 ]
Symptoms atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries
The presence of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is not always suspected, since the pathology often proceeds almost asymptomatically, or the symptoms are varied and non-specific. In most patients, the first signs appear only after significant blockage of the artery - that is, in the late stages of development. Taking this into account, doctors try to pay attention to risk factors in order to promptly suspect atherosclerosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. Obvious signs of the disease can be considered ischemic strokes of varying scale and general cerebral manifestations.
- Transient ischemic attacks develop when small particles of atherosclerotic deposits break off and block a small cerebral vessel that supplies a certain area of the brain. This area stops receiving nutrition and dies. Possible symptoms include temporary paralysis of the limbs (lasting from several minutes to several hours), speech and memory problems, sudden temporary deterioration of vision in one eye, sudden dizziness, and fainting. The occurrence of such attacks is a serious indication of the risk of developing a stroke in the near future. To prevent complications, the patient should immediately consult a doctor.
- Acute ischemic cerebral circulatory disorder is an unfavorable consequence of acute occlusion of the internal carotid artery and entails the death of nerve cells with partial loss of some brain functions. Every third patient dies, and every second becomes severely disabled.
- Chronic cerebral circulatory failure is caused by a deficiency of blood supply to brain structures, which is caused by arterial stenosis. Brain cells are overstrained, which affects the function of intracellular mechanisms and intercellular connections. The symptoms cannot be called specific: patients complain of a feeling of noise in the head, frequent dizziness, the appearance of "flies" in the eyes, an unsteady gait, etc.
First signs
The intensity and richness of the clinical picture may vary, but the most common signs are:
- Headache is experienced by the vast majority of patients with carotid artery atherosclerosis. Its occurrence indicates a nutritional deficiency in the brain structures, which is associated with insufficient blood supply. At first, patients report episodic, transient discomfort. Over time, the pain intensifies, attacks become longer and more frequent, and begin to bother several times a day. After taking analgesics, the problem does not disappear completely and for a short time. Pain characteristics: piercing, boring, pressing, with predominant localization in the forehead, temples and crown (sometimes - over the entire surface of the head).
- Dizziness may occur on its own or in combination with an attack of headache. This symptom indicates a growing trophic disorder in the cerebral structures, as well as problems in the frontal-temporal lobes and cerebellum. Additionally, spatial orientation may be impaired, and performance may decrease. In advanced cases, the patient tries to lie down more to alleviate the condition. An attack of dizziness can last from 2-3 minutes to several hours. The frequency is individual. As the situation worsens, the symptom worsens.
- Paroxysmal nausea and vomiting that do not bring relief are also a sign of nutritional deficiency in the brain. Vomiting urges are usually single, less often – multiple.
- The state of asthenia, fatigue, and sometimes drowsiness manifests itself against the background of a decrease or increase in blood pressure. Weakness and exhaustion can be present at any time of the day and even in the morning after waking up. The condition is often accompanied by general inhibition, deterioration of external reactions, and inattention. To avoid dangerous situations, such patients are not recommended to drive a car, work with various mechanisms, or simply leave the house without an escort.
- Sleep disorders manifest themselves in the form of frequent awakenings, after which it is difficult for a person to fall asleep. In the morning, the patient feels exhausted, not rested, and this continues for a long time. Without treatment, there is no talk of independent functional restoration of the nervous system.
- Progressive mental disorders are most often manifested by neurotic syndromes: obsessive-compulsive, hypochondriacal, anxiety disorders. Patients are troubled by deep and long-term depressive states that are not amenable to psychotherapeutic correction. In case of organic cerebral damage, serotonin production is suppressed, which requires appropriate therapy. However, without direct treatment of carotid atherosclerosis, functional recovery cannot be achieved.
- Myasthenia occurs when there are disturbances in the frontal lobe. Patients experience muscle rigidity (tension) against the background of decreased motor activity. A person experiences difficulties when trying to get out of bed, walk, etc.
- Intellectual problems and memory impairment are detected in the early stages in approximately 4 cases out of ten. And as the pathological process progresses, mental disorders are detected in 98% of patients. Symptomatic disorders such as regular forgetfulness, mental retardation, absent-mindedness are noted. A person cannot concentrate for a long time, thinks for a long time, loses the ability to multitask. The development of dementia is unlikely, but even minor cognitive disorders negatively affect the quality of life. Such changes are especially noticeable in people whose professional activities are associated with mental stress. [ 12 ], [ 13 ], [ 14 ]
- Numbness of the limbs, paralysis, inability to perform motor activity, deterioration of tactile sensitivity are rare, occurring in only 1.5% of cases (with the development of pre-stroke conditions).
- Problems with vision and hearing manifest themselves in the form of loss of visible zones (scotoma), incorrect color perception, loss of the ability to estimate distances to an object, bilateral loss of vision (transient blindness). Among hearing disorders, such symptoms as loss of auditory sensitivity and the appearance of ringing in the ears dominate.
- Neurological disorders are detected in the form of unpredictable aggressiveness, tearfulness, hallucinations. Such disorders occur in attacks and pass after a short time.
- Problems with potency in men, menstrual cycle disorders in women, reproductive disorders are usually associated with a decrease in the level of neurotransmitters and hormones in the body, insufficient pituitary and hypothalamic function. Symptoms become much worse over the years, which is due to the increasing deficiency of estrogens and androgens.
Initial manifestations of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries
Clinical symptoms largely depend on the stage of the disease:
- At the initial stage of development of atherosclerosis of carotid arteries, the problem may appear only after physical activity or emotional overload, with the disappearance of symptoms at rest. Patients complain of increased fatigue, lethargy, weakness, difficulty concentrating. Some patients have sleep disorders - mainly insomnia appears, followed by daytime sleepiness. Headache, noise, memory problems are characteristic.
- As the pathological process progresses, hearing and vision may be impaired, paresis and paralysis may occur, headaches and dizziness may occur, mood becomes unstable, and depressive states may develop.
- In advanced cases, there is a disruption of the functions of the limbs and some organs, and ischemic processes develop. The ability to orient oneself in space and time is lost, and memory often suffers. These disorders become irreversible.
Stages
Currently, specialists distinguish the following basic stages of the disease:
- Formation of lipid elements and bands. The first stage consists of damage to the endothelial layer of the arterial vessel, retention and accumulation of cholesterol particles in the damaged niches. An aggravating factor in this case is high blood pressure. Lipoprotein molecules are absorbed by macrophages and transformed into foam cells.
- Formation of a fibrous element. As foam cells accumulate, growth factors are released, which causes vigorous division of smooth muscle fiber cells and the production of elastin and collagen fibers. A stable plaque is formed, covered with a dense fibrous capsule, having a soft fatty core. Gradually, the plaque increases, narrowing the vascular lumen.
- Plaque enlargement. As the pathological process progresses, the fatty core increases, the fibrous capsule becomes thinner, thrombi form, and the arterial lumen becomes blocked.
If we talk about the internal carotid artery, then the thrombotic element on its wall can break off, blocking smaller diameter vessels. Often such vessels are the middle, anterior cerebral artery, and an ischemic stroke develops.
Forms
Atherosclerosis can have different origins, for example:
- hemodynamic - if it occurs as a result of a prolonged increase in blood pressure;
- metabolic – if it develops as a result of metabolic disorders (disorders of carbohydrate or lipid metabolism, or endocrine diseases);
- mixed – in the case of development as a result of the combined action of the listed factors.
In addition, the disease can be stenotic and non-stenotic, which depends on the stage of development of the pathology. Non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries practically does not manifest itself in any way: the term means that the blockage of the lumen by cholesterol deposits does not exceed 50%. This pathology can be suspected only by a slight systolic noise in the area of the vessel projection. In some cases, there is a need for conservative treatment.
Stenosing atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is the next stage of the disease, in which the arterial lumen is blocked by more than 50%. Signs of cerebral "starvation" appear with further gradual development of chronic ischemia or discirculatory encephalopathy. The final stage of stenosis is occlusion of the carotid artery.
The criteria for classifying arterial stenosis are defined as follows: normal (<40%), mild to moderate stenosis (40–70%), and severe stenosis (>70%).
Atherosclerosis is insidious because it is initially asymptomatic: the patient does not suspect anything until acute pathological conditions occur. [ 15 ], [ 16 ] Cognitive function largely depends on the degree of carotid artery stenosis. Patients with severe carotid artery stenosis always had a lower minimum mental state score compared to the mild to moderate carotid artery stenosis group (40–70%). [ 17 ] Patients with carotid artery stenosis often experienced minor cognitive problems, but not severe enough to affect daily activities. [ 18 ]
Depending on the localization of the lesion, atherosclerotic lesions of the carotid arteries are of the following types:
- Atherosclerosis of the internal carotid arteries is a lesion of the paired large artery of the neck and head from the bifurcation zone of the common carotid artery: it is there that it divides into internal and external branches. In turn, the internal carotid artery has several segments: cervical, petrous, segment of the lacerated opening, as well as cavernous, sphenoid, supracuneous and communicating segment.
- Athrosclerosis of the external carotid artery is a lesion of the section from the common carotid artery at the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage upwards, behind the digastric and stylohyoid muscles. At the neck of the articular mandibular process, the external carotid artery divides into the superficial temporal and maxillary arteries. In turn, the external carotid artery has anterior, posterior, medial and terminal branches.
- Atherosclerosis of the common carotid artery is a lesion of a paired vessel that begins in the chest, rises vertically and exits into the cervical region. The artery is then localized in the area of the anterior part of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae, on the side of the esophagus and trachea, behind the sternocleidomastoid muscles and the pretracheal plate of the cervical fascia. The common carotid artery has no branches and only at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage is it divided into the external and internal carotid arteries.
- Atherosclerosis of the right carotid artery involves damage to the section of the vessel from the brachiocephalic trunk to the bifurcation zone.
- Atherosclerosis of the left carotid artery begins from the aortic arch along the vessel to the bifurcation zone. The left carotid artery is slightly longer than the right one.
- Atherosclerosis of the carotid and vertebral arteries is a common combination that develops in older people. A characteristic feature of this pathological syndrome is drop attacks - sudden falls that are not accompanied by loss of consciousness, occurring immediately after a sharp turn of the head. The vertebral arteries are branches of the subclavian arteries that form the vertebral-basilar basin and provide blood supply to the posterior cerebral regions. They begin in the chest and go to the brain in the canal of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae. When merging, the vertebral arteries form the main basilar artery.
- Atherosclerosis of the carotid artery bifurcation is a lesion of the branching section of the common carotid artery, which is localized in the middle of the base of the carotid triangle along the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscles at the upper line of the thyroid cartilage. This location of the pathology is considered the most common.
Complications and consequences
As a result of carotid artery stenosis, cerebral blood supply gradually deteriorates, which can lead to the development of a stroke - a circulatory disorder in the brain. A stroke, in turn, is accompanied by various motor and sensory disorders, up to paralysis, as well as speech disorders.
Often, a plaque or part of it, or a thrombus breaks off from the surface of the inner wall of the carotid artery, which also leads to blockage of smaller vessels and ischemia of a part of the brain. In most cases, a stroke develops acutely, without any initial symptoms. In about 40% of cases, this complication ends in death.
The risk of stroke increases significantly as the pathology progresses and the size of atherosclerotic deposits increases. Complications may arise due to increased blood pressure, excessive physical or emotional stress.
A prolonged ischemic state of the cerebral cortex, caused by stenotic atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries, entails the development of atrophy of this structure with the subsequent appearance of atherosclerotic dementia.
Other adverse effects may include the following cerebrovascular pathologies:
- ischemic encephalopathy;
- ischemic cerebral infarction;
- hemorrhagic cerebral infarction;
- intracranial hemorrhages;
- hypertensive cerebral pathologies.
Ischemic encephalopathy is caused by a prolonged state of ischemia due to stenosing atherosclerosis. Typically, ischemic damage to nerve cells (damage to pyramidal cells of the cortex and Purkinje cells of the cerebellum), resulting in coagulation necrosis and apoptosis. Dead cells undergo gliosis.
Diagnostics atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries
If a person already has a clinical picture of atherosclerotic changes in the carotid arteries, then it becomes much easier to suspect the pathology. But at the initial stage of development, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, and it can be detected only after studying laboratory blood parameters.
Diagnostic measures at any age begin with an initial examination and anamnesis. During the survey, the doctor finds out the presence of provoking factors, chronic pathologies, suspicious symptoms. During the examination, he pays attention to the condition of the skin, and listening makes it possible to assess the heartbeat, breathing, etc. In addition to the initial examination, laboratory tests are prescribed - in particular, blood biochemistry, lipid spectrum analysis. Venous blood is taken on an empty stomach: the level of cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density and high-density lipoproteins is assessed in the blood serum. It is equally important to find out the glucose content in the blood.
Comprehensive laboratory tests include the following analyses:
- Complete lipid profile:
- The total cholesterol indicator is an integral value demonstrating the quality of cholesterol metabolism by blood lipoproteins. When the total cholesterol in the blood increases above 240 mg/dl, there is a high risk of developing cardiovascular pathologies.
- Cholesterol/low-density lipoproteins is an indicator that determines coronary risk. Normally, the concentration should not exceed 100 mg/dl.
- Apolipoprotein B is the basic protein component of atherogenic lipoproteins, the indicator of which reflects their total amount.
- Cholesterol/high-density lipoproteins.
- Apolipoprotein A1 is the basic protein component of high-density lipoproteins.
- Triglycerides are esters of the organic alcohol glycerol and fatty acids, the increase of which increases the risk of developing cardiovascular pathologies. The optimal indicator is up to 150 mg/dl.
- C-reactive protein is a kind of marker of the acute inflammatory phase. Its concentration reflects the degree of systemic inflammatory reaction. Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries is also an inflammatory process occurring with low intensity.
A microscopic specimen of venous blood can be used to determine the polymorphism of the endothelial synthase gene, an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of nitric oxide from L-arginine. Deterioration of the enzyme function leads to a disorder in the processes of vascular expansion and can participate in the development of atherosclerosis. In addition, polymorphism of the genes of blood coagulation factors V and II is determined to assess the individual risk of cardiovascular pathologies.
Instrumental diagnostics is most often represented by the following methods:
- Electrocardiography – demonstrates changes in the myocardium and in the work of the heart in general.
- Daily Holter ECG monitoring allows you to track the functional capacity of the heart, identify arrhythmia and ischemic changes in the myocardium.
- Exercise ECG. [ 19 ], [ 20 ]
- Bicycle ergometry – helps to assess the function of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems during physical activity.
- Echocardiography using ultrasound vibrations.
- Invasive coronary angiography. [ 21 ], [ 22 ]
- Coronary CT angiography. [ 23 ], [ 24 ]
- Nuclear perfusion imaging. [ 25 ]
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the heart. [ 26 ], [ 27 ]
Ultrasound diagnostics is an accessible and simple way to assess the condition of the carotid arteries. It is possible to use such procedures as Dopplerography and duplex scanning. Dopplerography allows one to examine the speed of blood circulation and determine its disorders. Duplex scanning evaluates the vascular anatomy, wall thickness and size of atherosclerotic deposits. Of course, the second option is more informative. [ 28 ]
Recently, three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound has been used to measure plaque volume. Plaque volume can be used as a monitoring tool for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Plaque volume is known to increase without treatment and decrease with statin therapy. [ 29 ] 3D ultrasound is considered useful for plaque monitoring and may also be useful for evaluating new treatments. [ 30 ]
Differential diagnosis
Given the frequent asymptomatic course of carotid atherosclerosis, it is recommended that doctors pay attention to existing risk factors and the presence of a hereditary predisposition: for this purpose, information should be collected from the patient about previous cerebrovascular accidents and transient ischemic attacks, pathologies of other vascular pools, hereditary hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, bad habits, etc. Atherosclerosis should also be differentiated from other arterial pathologies:
- stratification;
- non-specific aortoarteritis;
- pathological curvature of the internal carotid artery.
During the external examination, attention should be paid to the neurological status: the presence of hemiparesis, speech disorders. It is also necessary to listen to the carotid bifurcation zone to determine the characteristic systolic noise.
Asymptomatic patients in whom carotid atherosclerosis may be suspected should undergo duplex ultrasound scanning.
Who to contact?
Treatment atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries
When prescribing treatment for atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries, doctors try to adhere to the following principles:
- minimizing cholesterol entering the bloodstream and reducing its production by cells by normalizing nutrition with the exclusion of cholesterol-containing foods;
- acceleration of the removal of cholesterol and its metabolic products from the circulatory system;
- normalization of hormonal levels in women during menopause;
- treatment of infectious and inflammatory processes.
For more information on the treatment of carotid artery atherosclerosis, read this article.
Prevention
Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries cannot be cured completely, it is only possible to stop the development of the disease. Therefore, it is much easier to think in advance and prevent the development of the pathology at a young age. This also applies to those people who are at risk - for example, those with genetic disorders or unfavorable heredity. Experts explain: many of us tend to think that atherosclerosis affects only older people, but this is not true. The disease begins to develop in youth. And the main point of prevention is a healthy lifestyle. [ 31 ], [ 32 ]
- Scientists have proven that the unhealthy amount of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood largely depends on the presence of physical activity. And increased lipid content in the blood is the start of the development of atherosclerosis. With regular physical activity, the function of the cardiovascular system as a whole improves, ischemic processes are prevented. At the same time, there is no need for intense exercise: it is enough to simply walk, swim, play active games, ride a bike.
- Proper nutrition is the most important stage of prevention. To maintain health, you should “forget” about the existence of such products as fatty meat, lard, lard, offal, heavy cream, margarine and butter. The basis of the diet should be cereals, vegetables and greens, berries and fruits, low-fat cottage cheese, vegetable oils, fish and seafood, nuts and beans. It is also advisable to significantly reduce the consumption of salt, which provokes an increase in blood pressure, as well as sugar and sweets, which can give impetus to the development of diabetes and obesity.
- It is important to maintain normal body weight, not to overeat, and to monitor the caloric content of the diet. Excess weight is a risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries: to prevent the occurrence of pathology, you need to organize proper nutrition and be physically active.
- Bad habits, in particular smoking, have an extremely negative effect on the condition of the heart and blood vessels: blood pressure increases due to vascular spasms, the walls of the vessels become fragile, microdamages appear, contributing to the "sticking" of atherosclerotic plaques to the inner walls. As for alcohol abuse, it contributes to the disruption of the liver and pancreas, which entails a disorder of fat metabolism. To prevent the development of pathological processes, it is necessary to eradicate bad habits as early as possible.
- Starting at age thirty, you should monitor your cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood glucose levels by having them tested regularly. You should also visit your doctor regularly for preventive examinations and diagnostics.
Forecast
The brain is a complex structure capable of controlling various functions of the human body. If there are obstacles to the blood flow to certain brain areas responsible for certain functions, the corresponding organs and body parts stop working normally. In this situation, the prognosis depends on the degree of damage to the stenotic vessel and the size of the affected area of the brain. The consequences can be different, from temporary transient disorders to the death of the patient. The most common outcomes are motor disorders, muscle weakness or paralysis, problems with speech, swallowing, urination and defecation, pain and convulsions, neurological disorders.
Provided that the therapy is carried out in a timely manner, the outcome is considered relatively favorable. If the form of the disease is advanced, then relative recovery can be spoken of only in half of the cases. [ 33 ]
Atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries with significant blockage of the vascular lumen can lead to the development of an acute condition - in particular, a stroke, in which the risk of death is especially high.

