
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Smear analysis for flora: how to prepare, what shows?
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 05.07.2025
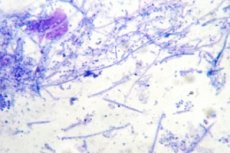
Among the many laboratory studies, there is also one called a smear for microflora - this is an analysis that determines the presence of bacteria at the site of taking the material, and also identifies them. The flora in the smear can be diverse, depending on where the smear is taken and the presence of pathology in this area. Thus, it is possible to diagnose inflammatory processes or diseases that are transmitted sexually.
Taking a smear is done quickly and without any particular discomfort. To evaluate the flora in the smear, the removed material is stained, making it easier to distinguish microorganisms.
What does a smear test include?
Experts distinguish several diagnostic types of determining flora in a smear:
- A general smear is used to assess the vaginal cleanliness of patients. What does it include:
- indicators of the state of epithelial cells;
- the presence of diseases caused by microbial or fungal infections.
Bacterioscopy allows us to detect sexually transmitted diseases.
- A smear test for latent infection is done to identify diseases that occur without specific symptoms, but can cause a number of long-term complications, such as infertility. The flora is examined using PCR - such a diagnostic reaction allows you to detect an infectious agent that is not isolated during a general smear test.
- A smear with oncocytology (the so-called Pap test) is performed to exclude oncological processes localized in the cervix. It is no secret that diagnostics of tumors at the initial stages of development often allows for successful treatment of the disease. In addition, this test helps to identify almost all inflammatory processes, epithelial dysplasia. Doctors advise all female patients to undergo such diagnostics once a year.
In addition, a smear is obtained from the urethra (in male patients), from the pharynx and nose, from the ear - depending on what problem is suspected.
Indications for the procedure of flora in the smear
Determination of flora in a smear is included in the list of mandatory tests during routine gynecological examinations. The procedure is performed by a doctor during a gynecological examination. Material can be taken from the vaginal walls, from the cervix or from the urethra.
The study helps to find the cause of many health problems – for example, it is possible to detect an inflammatory reaction or a sexually transmitted infection. Evaluation of the flora condition is called bacterioscopy in medical terminology.
In gynecology, a smear is taken in cases where identification of the following diseases is required:
- microbial vaginosis;
- inflammatory reaction - vaginitis;
- fungal infection - candidiasis;
- diseases that are transmitted sexually - gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, etc.
The study is conducted in order to determine the correct diagnosis if a woman voices the following complaints:
- itching, discomfort, burning inside the vagina;
- painful sensations during sexual intercourse;
- the appearance of unhealthy discharge, often with a characteristic odor;
- pain in the lower abdomen.
In addition, a smear test is mandatory at the planning stage and during pregnancy, as well as after antibiotic therapy.
A smear test for flora is always taken from men when visiting a urologist or venereologist, as well as when undergoing a medical examination. This type of examination is especially necessary:
- in case of atypical discharge from the urethra;
- in case of male infertility and suspicion of it;
- for sexually transmitted diseases, or if there is a suspicion of them.
A swab from the nasal cavity and pharynx is relevant:
- in the presence of plaque on the tonsils, with tracheolaryngitis, with abscesses in the tonsil area, with infectious mononucleosis;
- if tuberculosis is suspected;
- for chronic rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis;
- for frequent respiratory infections.
A smear is also taken if diphtheria or whooping cough is suspected.
Determination of the microflora in the ear is carried out in any variant of purulent otitis, as well as in serous otitis, to identify the causative agent of the disease.
Preparation
Gynecological determination of flora in a smear is carried out no earlier than three days after the end of menstrual flow.
A smear test for flora is not taken during menstruation! The presence of bloody discharge on the walls of the vagina distorts the results of the analysis, which in most cases may be unreliable.
A smear test for flora is not taken on the last day of menstruation for the same reason. The optimal period for conducting the study is from the tenth to the twentieth day of the monthly cycle.
To avoid errors when conducting analysis, you should also follow other important recommendations:
- a couple of weeks before the study, complete any treatment with antibiotics and antifungal drugs;
- a couple of days before the examination, refrain from using any intravaginal products - douches, tampons, suppositories, irrigations, ointments, etc.;
- avoid sexual intercourse for a couple of days;
- Do not take a bath the day before the test, and take a shower the morning before the test without adding any detergents.
Taking a smear from the male urethra also requires certain preparation:
- a couple of days before the diagnostic procedure, you must refrain from sexual intercourse;
- In the morning on the day before the examination you need to take a shower;
- It is not advisable to urinate a couple of hours before visiting the doctor;
- One week before the examination, you must stop taking all antibacterial and antifungal medications.
If you plan to take material from the nasopharynx, then here too you need to focus on the preparatory stage, which includes the following conditions:
- a couple of hours before the diagnosis, you should not eat or drink anything;
- On the day of diagnosis, you should not brush your teeth, irrigate or rinse your throat, use antimicrobial sprays, or take antibiotics;
- If it is planned to collect material from the nose, then before the examination you should not apply ointments to the mucous membrane, drip solutions into the nose or spray.
Taking a smear from the ear is performed before starting antibiotic therapy.
Who to contact?
Technique of flora in the smear
- A doctor takes a smear of flora from women in a gynecological office or in a specially equipped laboratory. The diagnostic manipulation includes the following stages:
- the patient is positioned in a gynecological chair;
- the doctor gains access to the vaginal cavity and cervix using sterile speculums;
- the doctor removes material from the posterior vaginal fornix, places it on a special laboratory glass and sends it to the laboratory;
- The smear is stained with methylene blue, after which the laboratory technician determines the type of bacteria and details the composition of the flora.
In most cases, a gynecological smear is taken from three areas at once: the exit of the urethra and paraurethral tract, the vaginal walls, and the cervical canal. If the material is taken from only one of the listed areas, this must be indicated on the form and on the slide: C - from the cervix, U - from the urethra, V - from the vagina.
- A smear test for flora during pregnancy is taken at least three times: when a woman registers for pregnancy, and also at 30 and 36 weeks of gestation. In case of a threat of miscarriage, polyhydramnios, intrauterine infections, the doctor may insist on additional material collection for analysis. The procedure for taking a smear in pregnant women is no different from that in the absence of pregnancy.
- A smear test for flora in men is taken quite quickly - literally in a couple of minutes. A thin probe is inserted into the urethra, approximately 4 cm deep, after which it is removed by rotation.
- A nasopharyngeal swab is performed simply using a cotton swab, which is inserted into the nose or throat area and pressed against the mucous membrane.
- A smear from the ear is taken with a cotton swab and applied by rolling onto a laboratory glass. A separate swab and glass are used for the left and right auditory canals.
Normal performance
The vaginal cavity should normally contain quite a few varieties of microbes, which make up the normal vaginal flora. The largest part of such microorganisms are lacto and bifidobacteria, which live on the epithelial tissue. Such bacteria produce acidic and alcoholic compounds, due to which an acidic vaginal environment is maintained. Of considerable importance among other microflora are enzymes, for example, lysozyme, which prevents the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms.
Below in the table we will display the types and quantities of microorganisms that normally inhabit the vaginal microflora:
Representatives of flora |
The number, which is determined by CFU/ml |
Bifidobacterium |
From 10 3 to 10 7 |
Lactobacillus |
From 10 7 to 10 9 |
Clostridium |
No more than 10 4 |
Staphylococcus |
From 10 3 to 10 4 |
Corynebacterium |
From 10 4 to 10 5 |
Peptostreptococcus |
From 10 3 to 10 4 |
Propionibacterium |
No more than 10 4 |
Mobileuncus |
No more than 10 4 |
Streptococcus |
From 10 4 to 10 5 |
Enterobacteria |
From 10 3 to 10 4 |
Bacteroidetes |
From 10 3 to 10 4 |
Prevotella |
No more than 10 4 |
Porphyromonas |
No more than 10 3 |
Candida |
No more than 10 4 |
Ureaplasma |
No more than 10 3 |
Mycoplasma |
No more than 10 3 |
Fusobacterium |
No more than 10 3 |
Veillonella |
No more than 10 3 |
The specified parameter CFU denotes the number of units capable of forming colonies in a milliliter of nutrient medium.
The device for analysis
A smear test for microflora (using a glass slide) is a laboratory analysis based on examining the biomaterial under a light microscope. No special equipment is required to perform the analysis – it is enough to have a high-quality optical device that visualizes the smallest details in the smear. The main indicators of a high-quality microscope are the appropriate optical magnification, the presence of the necessary attachments and lighting devices.
With the help of a good microscope it is possible to:
- characterize the microflora in the area under study;
- see the presence of inflammation, assess its degree;
- identify the direct causative agent of the disease, or detect indirect signs of the presence of a certain microorganism.
In order for the analysis to be carried out with the highest quality, it is necessary to submit the material to a verified clinic - this can be a state or private medical institution. The quality of the study must be confirmed by the following factors:
- compliance with all preparatory stages before the collection of biomaterial;
- availability of modern equipment and high-quality reagents;
- availability of relevant specialists – both doctors and laboratory technicians.
How long does it take to do a smear test?
There is no clear answer to this question. The length of the waiting period for the result depends on the area where the material was collected and what pathogen is being cultured. Thus, the answer may be ready in 1-3 days, less often - in 7 days, and in some cases - even within two weeks (if there is a need to re-culture the samples on other media).
More precise information about the waiting time for results should be requested from the clinic where the request for a smear test was received.
Raising and lowering of values
The form with the test results can be given directly to the attending physician: he will decipher the indicators, make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. But in some cases, the form is given "in hand" to the patient, who has a number of natural questions, for example: how to understand the information provided? What can these numbers and letters mean, is everything okay with me?
Of course, it is better to make an appointment with a doctor who will explain the results of the study in detail. If the desire to figure it out on your own still does not go away, you can turn to the following indicative interpretations:
- The absence of flora in the smear is extremely rare and in the vast majority of cases indicates prolonged treatment with powerful antibiotics. Modern antibacterial drugs are capable of destroying not only pathogenic but also healthy flora. The absence of microorganisms in the smear requires long-term and painstaking restoration of the bacterial balance.
- A large amount of flora in a smear can be both normal and pathological. It all depends on which flora predominates - healthy or pathogenic. A high level of pathogenic microorganisms, a lot of mucus and epithelial cells indicate an inflammatory process: this condition requires mandatory therapy. Urgent treatment is prescribed for mass reproduction of pathogenic flora, in the presence of specific bacteria that cause certain diseases - for example, gonorrhea or trichomoniasis.
- Leukocytes are always present in a smear on flora, since these are the cells that primarily provide protection of mucous tissues from infection. The norm of leukocytes in a smear on flora is 15-20 (in the urinary tract up to 5, in the vaginal cavity - up to 10, and in the cervix - up to 20 units). During pregnancy, an increase in this level by another 5 units is allowed. If the number of leukocytes exceeds the permissible norm, then most often the presence of an inflammatory process in the tissues is suspected. After additional studies, the doctor makes a diagnosis of vaginitis, colpitis, cervicitis, etc. With pronounced inflammatory reactions, the leukocyte count increases several times - for example, in patients with gonorrhea or trichomoniasis, an especially large number of such cells are found.
- Red blood cells should be absent in a smear of flora in a healthy person. The reasons for detecting red blood cells may be as follows:
- mechanical damage to the mucous membrane at the time of taking the smear;
- the presence of an active phase of the inflammatory process;
- the presence of benign or malignant processes in tissues.
Other auxiliary diagnostic methods are usually used for clarification. If there is a suspicion of damage to the mucous membrane during medical manipulations, the smear is taken again.
- Flat epithelium is always present in a smear for flora if the woman being examined is of childbearing age. With a sharp change in hormonal balance, as well as during menopause, the number of epithelial cells in the smear decreases. With the onset of the menopause, the material mainly contains lower-layer vaginal epithelium, represented by basal and parabasal cells. If such cells appear in the smear of patients of reproductive age, this may indicate a high content of male sex hormones, or a pronounced inflammatory process.
- Cylindrical epithelium in a smear on flora can be detected only if the material is taken from the cervical canal. The fact is that the mucous tissue of the urogenital tract consists of flat epithelium, and cylindrical epithelium is present only in the cervical canal. Any change in the amount of cylindrical epithelium indicates cardinal disturbances in the patient's hormonal balance, or the development of an inflammatory process.
- Mucus in a smear on flora is normally present in the vagina and cervix - in small quantities, but in the material taken from the urethra, there should be no mucus. Usually, an adequate level of mucus is described as a moderate or scanty amount. Strands of mucus in a smear on flora indicate a high probability of an inflammatory process, but are not a 100% sign of it, so this indicator is considered only in conjunction with other laboratory values.
- Often, the results of the study indicate such a concept as phagocytosis. This process is the detection and destruction of pathogenic microorganisms by leukocytes. Phagocytosis in a smear on flora is mostly incomplete, as evidenced by a large number of unprocessed bacterial cells inside leukocytes. This can be observed when an infection is added, as well as after stress and against the background of nutritional disorders.
- Cytolysis in a smear on flora indicates the presence of a non-inflammatory reaction in the vaginal cavity. Such a reaction occurs due to increased activity of a separate type of lactic acid bacilli that release hydrogen. An uncontrolled increase in the number of such bacilli causes a shift in the vaginal environment to the alkaline side, with subsequent cytolysis (disintegration) of epithelial cells.
- An uncommon component in a smear may be fibrin, a protein substance present in blood plasma. Fibrin in a smear for flora indicates the development of an inflammatory reaction in the tissues.
- Detritus in a smear on flora means the total amount of residual particles of microorganisms and dead cellular structures that have accumulated as a result of various processes on mucous tissues. In small amounts, detritus is present on the skin and mucous membranes, in the intestinal cavity. If a significant amount of detritus is detected, this indicates a sharp and massive death of a large number of microorganisms in one area. This happens when taking large doses of antibiotics, with allergic processes, with a sharp imbalance of microflora.
Flora species in smear
- Coccal flora in the smear is also allowed - in small quantities. These microorganisms - cocci - are distinguished by their spherical configuration. In no case should there be more of them than Doderlein's rods: such a situation indicates a pronounced weakness of the immune defense or the development of an inflammatory reaction. Cocci can be Gr(+) and Gr(-). The former include enterococci, staphylococci, streptococci, and the latter - gonococci.
- Coccobacillary flora in a smear is primarily detected in vaginal dysbacteriosis, against the background of a decrease in the number of lactobacilli. Coccobacilli are microorganisms that resemble something between cocci and bacilli in shape. Bacteria of this type include hemophilic bacillus, gardnerella, chlamydia.
- The rod-shaped flora in the smear is normally represented by lactic acid bacteria. There should be a lot of such bacteria, which indicates the presence of an adequate hormonal background and the absence of inflammatory processes. The vaginal epithelium produces glycogen, which serves as a nutrient for Doderlein's bacilli - this is what lactobacilli are called. During glycogen breakdown, lactic acid is released, which ensures the constancy of the acidic environment in the vaginal cavity. Such an environment serves as a natural protective barrier against many infections. With insufficient content of bacilli, the vaginal environment becomes more alkaline: in such a situation, a diagnosis of vaginal dysbacteriosis is made.
- Polymorphic rod flora in a smear indicates the presence and number of different types of microorganisms in the seized material. The norms of such an indicator are quite relative, since it is not considered by itself: it is taken into account in combination with other laboratory signs, which allows confirming or refuting a probable pathology.
- In healthy patients, an adequate vaginal smear is represented mainly by lactobacilli - acidophilic Gr.(+) microorganisms. However, in addition to them, other types of bacteria are also present on the walls - this is the so-called mixed flora, which may include various opportunistic microbes. Mixed flora in a smear in patients of reproductive age increases immediately before and after menstrual bleeding, or in case of ovarian dysfunction. Changes in hormonal balance can also lead to the appearance of mixed flora in girls and women during menopause.
- Soor in a smear on flora is an indicator indicating the presence of candidal infection (thrush). A positive soor requires the appointment of antifungal treatment.
- Lactomorphotypes in a smear for flora should be detected if the material was taken from the vagina or cervix. Lactobacilli are normally absent in a smear from the urethra. If the vaginal smear contains a large number of lactomorphotypes (lactobacteria), then the microflora is considered high-quality. If there are few lactobacilli, then measures should be taken to restore the normal microbial balance.
- Blastspores in a smear on flora indicate the presence of candidiasis or other fungal infection, which is treated like thrush.
- Fungi in a smear on flora can be detected in the form of mycelium and spores, which usually happens with candidiasis (the well-known thrush). If Candida in a smear on flora is detected in the form of spores, then this may indicate a latent thrush (the so-called "sleeping" infection). With the slightest violation of immune protection, the fungal infection is activated, and the thrush worsens: in this case, full-fledged micellar threads are detected in the smear.
- Pathogenic flora in a smear is the presence of microorganisms that cause a certain disease. That is, if the diagnosis indicates the presence of pathogenic bacteria, then pathology is definitely present.
- Opportunistic flora in a smear, unlike pathogenic representatives, does not always mean the presence of a disease. Opportunistic microorganisms (for example, cocci) are capable of provoking the development of a disease only under favorable conditions for them - for example, with a significant decrease in immunity.
- Mycelium in a smear on flora indicates a fungal infection process. Mycelium is the most active form of fungus, while spores are its inactive variety. Spores in a smear on flora can be present in healthy patients, but mycelium is only present in candidiasis.
- Pseudomycelium threads in a smear on flora indicate increased candidal reproduction. Pseudomycelium has the appearance of threads consisting of elongated cellular structures and blastospores. As a rule, the study determines pseudomycelium only in the acute period of candidiasis.
- Key cells in a smear on flora can be represented by epithelial cells surrounded by small rods. On a healthy mucous membrane such elements are absent. But in pathology, the appearance of key cells indicates that aerobic lactic acid microorganisms were suppressed by anaerobes, in particular, by the smallest rod flora. In such a situation, the diagnosis indicates the presence of microbial vaginosis.
- Aerobic flora in a smear may be represented by staphylococci, E. coli, streptococci - microorganisms that require oxygen to develop. Typically, such microbes are present primarily in the external genital area and in the intestinal cavity, and they enter the vaginal cavity due to poor intimate hygiene or unprotected anal-vaginal intercourse. The presence of aerobes in a smear most often indicates the development of aerobic vaginitis.
- Staphylococcus aureus is allowed to be present in a smear on flora and is normal, but not more than 5% of the total amount of microflora. With an increased content of staphylococcus aureus against the background of a decrease in the level of lactobacilli, we speak of an inflammatory reaction in the vagina or cervical canal.
- Diphtheroids in a smear on flora, found in small quantities, do not cause problems. However, with other disturbances of the microbial balance, these microorganisms are capable of causing pathology. Diphtheroid flora in a smear is usually represented by microbes that are similar to diphtheria bacilli. Excess of their number is considered a sign of microbial vaginosis.
- Gardnerella is detected in a smear on flora in case of vaginal dysbiosis, or so-called microbial vaginosis. Gardnerella are tiny rods that cause such an infectious pathology as gardnerellosis. The permissible content of gardnerella in a smear is no more than 10 5.
- Leptothrix in a smear looks like a thin gram-negative microorganism. Leptothrix itself does not cause disease, but can accompany other infections - for example, it is often detected against the background of trichomoniasis, candidiasis, chlamydia, as well as with a common imbalance of vaginal flora.
- Gonococci in a smear on flora can be found both in the urethra and in the vaginal cavity. The presence of these microorganisms indicates infection with gonorrhea - a disease that is transmitted sexually. The disease requires unambiguous treatment, and both sexual partners undergo a course of therapy.
- Corynebacteria in a smear on flora may be present in safe quantities. This is a type of gram-positive rod-shaped microbes, better known as the causative agents of diphtheria. These bacteria sometimes get into the vagina from the intestine and in large quantities can cause inflammatory processes.
- Actinomycetes in a smear on flora usually lead to a disease - actinomycosis, caused by ray fungi. Actinomycetes are able to live on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and eyes in the form of saprophytic flora, and under favorable conditions - for example, against the background of an inflammatory reaction, fungi are activated, actinomycosis develops.
- Trichomonas in a smear on flora can become the causative agent of vaginal trichomoniasis. Such microorganisms are voluminous single-celled bacteria equipped with a flagellum. In trichomoniasis, the laboratory technician can detect both whole cells and destroyed particles of microbes. In both the first and second situations, they speak of the presence of a trichomonas infection.
- Enterococcus may be present in a smear on flora in a certain amount - this microbe is considered opportunistic, so with adequate immunity and the absence of provoking factors, there is no need to be afraid of it. With active reproduction of enterococci, enterococcal infection occurs - such a pathology is usually treated with antibiotics prescribed by a doctor after an analysis of the sensitivity of the flora. The difficulty is that such an infection often has increased resistance to many modern antibacterial agents. Therefore, it is necessary to clearly know which antibiotic will help in a particular situation.
- Chlamydia in a smear on flora is often detected simultaneously with mycoplasma and ureaplasma. Large quantities of these microorganisms can disrupt the function of the reproductive organs and cause infertility. To confirm chlamydia and determine further treatment tactics, it is necessary to additionally conduct diagnostics using the PCR and ELISA methods.
- E. coli in a smear on flora are acceptable in small quantities. However, with mass reproduction of bacteria, problems arise, such as microbial vaginosis and other diseases. The pathology is usually cured completely, without further development of complications.
How to treat flora in a smear?
It should be noted that the flora itself does not require treatment: treatment procedures can be prescribed to the patient if the pathogenic flora becomes dominant, which leads to the development of various diseases. Sometimes it is enough to conduct a course of normalization of the microflora - for example, with drugs containing beneficial microorganisms (lactobacilli, live yogurt cultures, probiotics, etc.).
Such pathologies as gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, trichomonas and chlamydia always require treatment with special medications that affect the corresponding group of microorganisms. Treatment can be complex - injections, oral medications, suppositories, ointments, irrigations. In mild cases, it is possible to use only suppositories or creams.
The decision on the advisability of therapy, as well as the scale of treatment, is made by the attending physician based on tests and the existing clinical picture.
How to treat coccal flora in a smear?
Treatment usually consists of local use of medications for 7-14 days. Betadine is used most often in gynecology, but contraindications and side effects (for example, itching, irritation of the vaginal mucosa) are taken into account when prescribing.
Any common coccal flora requires the use of antibacterial drugs - Clindamycin, Metronidazole. Such drugs can be presented in any convenient dosage form: from tablets and aerosols to suppositories and creams.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe medications to activate the immune system, as well as probiotics.
If there are complaints of discomfort such as itching and burning, then antihistamines and antifungal drugs are added to the treatment (they are prescribed immediately after antibiotic therapy).
In case of minor coccal lesions, the doctor may do without antibiotics, replacing them with antiseptic solutions (for example, Chlorhexidine solution), as well as oral medications (for example, Lactobacillin suspension). In addition, women should douche with calendula, chamomile, and celandine infusion.
How to restore flora in a smear?
The initial stage of flora restoration consists of neutralizing pathogenic microorganisms. To cleanse mucous tissues from "extra" bacteria, the doctor most often prescribes local drugs - these can be vaginal suppositories or tampons soaked in medicinal solutions. Some patients need to additionally take antifungal drugs.
The second stage on the path to stabilizing the microflora is considered to be its saturation with lactobacilli and other microorganisms that are part of the healthy flora. For this purpose, special medications are prescribed, with simultaneous laboratory monitoring of the normalization process.
It should also be remembered that maintaining the flora within normal limits is impossible with persistent immune dysfunction, primarily at the local level. Therefore, many patients should additionally take immunocorrecting drugs, such as suppositories with immunomodulatory properties. Sometimes such treatment is carried out immediately before antibiotic therapy.
For the complete process of flora stabilization, one month is usually enough. This must be confirmed by laboratory tests - that is, after completing the course of therapy, the patient re-checks the flora in a smear.
Treatment of elevated leukocytes in a smear on flora
The norm of leukocytes in a smear for flora depends on the area where the material was taken. Usually, only a small number of them is allowed in a smear - up to 15-20 (in the urinary tract up to 5, in the vaginal cavity - up to 10, and in the cervix - up to 20 units). This indicator increases sharply in inflammatory reactions (colpitis, urethritis), and the higher it is, the more acute the inflammatory reaction. A slight increase in the value during pregnancy is also allowed - for example, up to 15-20 units can be found on the walls of the vagina, and this will be considered a variation of the norm.
If there is inflammation, the doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory therapy. The drugs are selected depending on the general characteristics of the laboratory results. As a rule, the treatment is combined and includes local action, general therapy and subsequent restoration of adequate flora.
Locally, douching (4-5 days) with Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, herbal infusions (chamomile, sage, calendula) is prescribed. It is recommended to introduce vaginal suppositories with an anti-inflammatory effect: the drugs of choice are often Hexicon, Betadine, Polygynax, etc. If a fungal infection was detected in the smear, the doctor will advise using antifungal suppositories, such as Clotrimazole, Livarol, Pimafucin, etc. Such suppositories should be inserted 1-2 times a day, and the course of therapy can be 1-2 weeks.
If laboratory tests indicate the presence of viruses, pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases, or latent sexually transmitted infections, then there is a need for systemic antiviral or antibacterial therapy.
The final step for successful treatment is the restoration of microflora. Vaginal suppositories or tampons soaked in probiotic solutions are used. Oral administration of restorative drugs for ½-1 month is also possible. At the end of the therapeutic course, a control assessment of the flora in a smear is carried out.


 [
[