
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Brain hydrocele in a newborn: symptoms, treatment
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
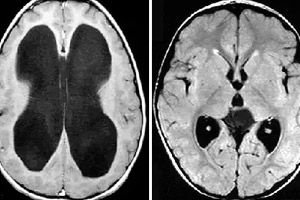
Increased levels of cerebrospinal fluid in the meninges is hydrocele. Let's consider the features of this pathology in children, causes, symptoms, treatment.
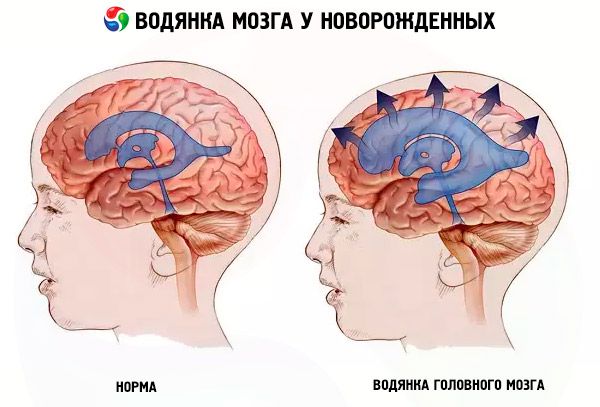
Hydrocephalus in newborns is a disease that most often develops in utero. Excessive amounts of cerebrospinal fluid fill the spaces between the meninges and penetrate into the ventricles of the brain. The disease is associated with diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy. Another reason is birth injuries, blows, tumors.
Neurological diseases are differentiated by the nature of their localization:
- External - cerebrospinal fluid accumulates around the brain at the base of the skull. Accompanied by expansion of the bones.
- Internal - fluid accumulates in the ventricles of the brain. Does not cause changes in the size of the baby's head.
- Mixed - accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid is observed both around the brain and inside its ventricles.
Normally, cerebrospinal fluid constantly washes the brain. This substance constantly circulates. It delivers nutrients from blood vessels to tissues and protects against damage. It affects the processes of respiration and blood circulation, maintains a normal environment around the brain. If the cerebrospinal fluid stagnates, accumulates under the meninges or in its ventricles, this leads to hydrocephalus.
Epidemiology
Medical statistics indicate that every 500th newborn suffers from hydrocephalus.
- The development of the disease in the fetus in 80% of cases is associated with intrauterine infections, in 20% these are malformations of the nervous system or genetic disorders.
- In newborns, hydrocephalus is most often associated with developmental defects of the brain or spinal cord, in 20% with birth injuries, and least often with tumors or developmental defects of the vessels that feed the brain.
- In children over 1 year of age, VGM most often develops due to tumor processes, hemorrhages, as a result of inflammatory damage to the brain or its membranes, after injuries, and least often due to hereditary problems.
Statistical data significantly facilitates the process of diagnosing the disease and allows for preventive measures to be taken to prevent it.
Causes of cerebral hydrocele in newborns
Hydrocephalus is a fairly frequently diagnosed pathology in children. The causes of hydrocephalus in newborns can be associated with congenital, that is, intrauterine and acquired factors.
Among the infectious causes of VMG, the following are distinguished:
- Herpes virus type 1 or 2.
- Toxoplasmosis.
- Cytomegalovirus.
- Neurosyphilis.
- Rubella.
- Epidemic mumps.
- Viruses and bacteria that cause meningitis and meningoencephalitis.
Congenital defects that cause disease:
- Arachnoid cysts.
- Anomalies of the cerebral veins.
- Narrowing of the channel connecting the ventricles of the brain.
- Congenital underdevelopment of the openings through which cerebrospinal fluid flows from the canal into the subarachnoid space.
- Arnold-Chiari syndrome is a disorder in which the volume of the posterior cranial fossa does not correspond to the structures that are inside it. This leads to them descending into the occipital foramen, where the brain passes into the spinal cord and oblongata. Such a displacement is dangerous because it infringes on the brain structures. This can lead to disorders of the vasomotor and respiratory centers, and even to death.
- Dandy-Walker syndrome is an abnormal development of the cerebrospinal fluid spaces and the cerebellum.
Oncological causes:
- Brain cancer
- Tumor lesions of the cerebral ventricles.
- Papillomas.
- Spinal cord tumors that limit the circulation or absorption of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Tumors of the skull bones.
- Choroid plexus meningiomas.
The disease may arise due to craniocerebral trauma sustained during the birth process. When identifying the cause of the disorder, the nature of its course and localization are taken into account.
Risk factors
Increased levels of cerebrospinal fluid in the spaces between the meninges, or in the ventricles of the brain themselves, occur for a variety of reasons.
The main risk factors for the birth of a child with hydrocele are:
- Infectious diseases suffered by a woman during pregnancy.
- Diseases of the mother's nervous system that are transmitted to the fetus.
- Use of drugs and alcohol, smoking.
- Genetic disorders of both parents.
- The baby was born before 35 weeks of gestation.
- The baby's weight is less than 1500 g.
- The mother in labor has a narrow pelvis, which makes childbirth difficult.
- During the birth process, a vacuum, forceps, or manual techniques were used to assist the newborn.
- During childbirth there was asphyxia or hypoxia of the fetus.
- The baby was born with intrauterine pathologies of internal organs.
The risk of developing hydrocephalus in the prenatal period is associated with the following factors:
- Rhesus conflict between mother and fetus (immune dropsy).
- Pregnancy against the background of severe forms of diabetes mellitus, anemia or gestosis.
- Cardiovascular pathologies or blood diseases in the fetus.
- Disorders of metabolic processes in the fetus.
- Placental malformations and umbilical cord lesions.
The above factors pose a high risk of the baby dying in the womb. That is why the pregnant woman should be under close medical supervision.
Risk factors for hydrocephalus in the postnatal period:
- Birth injuries and premature birth.
- Chromosomal abnormalities.
- Tumors of the spinal cord and brain.
- Meningitis, encephalitis.
Knowing the main risk factors of the disease, the pregnant woman and doctors should do everything to prevent its development. But in some cases, it is impossible to establish the true cause of the disease and the factors that led to its development.
Pathogenesis
A complex neurological disease in which the balance between absorption and production of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted has a specific mechanism of origin. Pathogenesis is associated with the peculiarities of the brain and the functions of the cerebrospinal fluid.
So, the brain is a blood-supplied structure of several cavities, i.e. ventricles. The ventricles are lined with vessels that are responsible for the formation of cerebrospinal fluid. All cavities communicate with each other, and the fluid circulates between them. The cerebrospinal fluid also washes the spinal cord. After which it enters the venous sinuses in the cranial cavity. The absorption of cerebrospinal fluid depends on the difference in pressure. In the sinuses, the pressure should be lower than the intracranial pressure.
Liquor is formed constantly. In newborns, it is synthesized in a volume of 40 to 150 ml per day. The fluid consists of leukocytes, lymphocytes, protein, electrolytes and other substances.
Cerebrospinal fluid performs the following functions:
- Protects the brain from injury because it is an incompressible fluid.
- Maintains balance with the water-electrolyte composition of the circulatory system.
- Due to oscillatory movements it affects the autonomic nervous system.
- Removes some substances from parts of the central nervous system.
- Maintains intracranial pressure at a constant level.
Disruption of these functions leads to a disorder in the formation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. It is possible that the flow of fluid may change along paths not intended for this. This leads to the development of hydrocephalus. Depending on the severity of the disorder and the pressure in the cranial cavity, various severity of the course of VGM and the corresponding symptoms may be observed.
 [ 16 ]
[ 16 ]
Symptoms of cerebral hydrocele in newborns
Increased cerebrospinal fluid content between the meninges, or in the ventricles of the brain itself, has various symptoms. The signs of the disorder depend entirely on the nature of its course:
- Acute – intracranial pressure increases rapidly, the condition worsens sharply (less than 3 days).
- Subacute – the pathological process develops over 3-6 months and leads to severe damage to brain structures.
- Chronic – the neurological problem develops extremely slowly and has increasing symptoms. This form is most often found in open hydrocephalus.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus in newborns also depend on its cause. Most often, hydrocephalus is diagnosed by the following signs:
- Decreased muscle tone.
- Frequent muscle cramps and tension.
- Accelerated growth and enlargement of the cranium.
- The size of the baby's head does not correspond to the proportions of the body and deviates from normal values.
- Frequent throwing back of the head.
- The fontanelle is enlarged in size, and the frontal part is greatly pushed forward.
- Setting sun syndrome (eyeballs are displaced downwards), strabismus.
- Spontaneous eye movement.
- Tremor of the limbs and chin.
- Poor weight gain and delayed psychomotor development.
- Frequent regurgitation.
- Anxiety, poor sleep, frequent crying.
- Lack of reaction to what is happening around.
Increased intracranial pressure in an infant causes severe headaches. At such moments, the child may put his hands to his head. Such signs should not be ignored. To detect the disease before the baby is born, routine ultrasounds are performed, and blood sampling from the umbilical cord or amniocentesis is also possible.
The clinical picture of hydrocephalus in children after one year is supplemented by the following pathological symptoms:
- Attacks of nausea and vomiting in the morning and evening.
- Epileptic seizures with loss of consciousness.
- Muscle hypertonicity.
- The face and forehead are covered with a venous network.
- Urinary incontinence.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- The fontanelle does not close, increases in size and swells.
- Visual acuity deteriorates, which can lead to blindness.
- Tendency to obesity.
As the disease progresses, mental and physical impairments become more noticeable. All of the above symptoms may occur not only with VGM, but also with other pathologies. A similar symptom complex is observed with malformations of the brain, various neoplasms. It is very important to identify the disorder at its early stages and begin treatment as quickly as possible.
First signs
A complex neurological disease has its own characteristic early signs. Hydrocephalus in newborns can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- Accelerated growth of the head circumference, which does not correspond to normal values. This is due to the growth of the brain, which pushes apart the bones and sutures of the skull from the inside, which have not yet healed.
- Increase in size and strong tension of the fontanelle. Normally, the fontanelle disappears by the first year of a child's life, but in case of disorder it can be noticeable up to 2-3 years.
- Bulging and disproportionate enlargement of the forehead.
- Involuntary oscillatory movements of the eyes, strabismus, nystagmus.
- Spider veins on the face.
- Convulsions, increased muscle tone in the limbs.
In addition, the newborn has slow psychomotor development. He often throws his head back, cannot hold it up, sit, or stand up. The baby often cries and is capricious for no apparent reason. Periodic touching of the head indicates severe headaches.
 [ 20 ], [ 21 ], [ 22 ], [ 23 ], [ 24 ]
[ 20 ], [ 21 ], [ 22 ], [ 23 ], [ 24 ]
External hydrocephalus in newborns
A neurological pathology in which certain disturbances occur in the ventricular system and in the space under the meninges is external hydrocephalus. In newborns and older children, this disease is associated with increased formation of cerebrospinal fluid or impaired outflow.
External hydrocephalus is extremely rare. It is characterized by the localization of excess cerebrospinal fluid in the subarachnoid space. At the same time, the cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles and spaces of the brain is normal. In most cases, external hydrocephalus is formed with atrophy of the brain.
External hydrocele can be congenital and acquired; there are also open, closed and ex vacuo forms.
- Open form – develops due to a disruption in the production and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. The cerebrospinal fluid spaces communicate normally with each other.
- Closed – characterized by the separation of cerebrospinal fluid-bearing spaces at different levels.
- Ex vacuo – is a consequence of the reduction of the brain parenchyma due to its atrophy or various pathologies of the nervous system. It can have a progressive, stabilizing and regressive course.
The external form of hydrocephalus can be caused by the following reasons: craniocerebral trauma, pathologies in the development of the central nervous system, disorders of the cervical vertebrae, diseases of the brain or its membranes, changes in the functioning of the brain vessels.
Symptoms of the disease are manifested by a sharp increase in head volume by 50%. Against this background, bone sutures diverge, the fontanelle and skin veins swell. The most dangerous is the moderate course of the disorder. This is due to the absence of obvious symptoms for several years. But then comes the moment when the baby's condition deteriorates sharply due to a violation of cerebral circulation.
MRI, CT, ultrasound, X-ray examinations, and various tests are used to diagnose the disease. Treatment can be either medicinal, i.e. conservative, or surgical.
Complications and consequences
Hydrocephalus in newborns is a serious disease that requires mandatory treatment. The consequences and complications of the pathology are manifested by various symptoms and depend on the patient's age:
- Newborns – increased excitability, sleep disturbances, developmental delays, mental abnormalities.
- Preschool age – speech problems, hearing and vision impairment, aggression, hysterical attacks, delayed psychomotor development, strabismus, stuttering.
- School age – various degrees of debility, personality disorders, poor memory, neuropathic disorders, frequent headaches, epileptic seizures, psychoemotional disorders.
Hydrocephalus can lead to disability. Delayed motor development, cerebral palsy, and seizures indicate physical disability.
The consequences and complications of VGM also depend on the treatment methods. After surgery, hematomas, pseudocysts, epileptic seizures of varying severity, and shunt dysfunction may form. A fatal outcome is also possible if the disorder takes a malignant course or is diagnosed too late.
 [ 29 ]
[ 29 ]
Diagnostics of cerebral hydrocele in newborns
Modern diagnostics of hydrocephalus in newborns is of primary importance for the treatment and further recovery of the baby. Medicine has developed many methods that are effective in identifying hydrocephalus. Let's consider the main ones:
- Neurosonography is an ultrasound examination of the brain through the fontanelle. The procedure is absolutely painless and safe. It is part of the complex of mandatory examinations for newborns in the first months of life. It reveals various pathologies at the earliest stages.
- MRI, CT and electroencephalography provide more detailed information about the state of the brain structures. Both methods are performed under general anesthesia.
- Ophthalmoscopy is an examination of the fundus of the baby's eye. If the optic discs are swollen, this indicates increased intracranial pressure, which may be a symptom of hydrocele.
- Lumbar puncture – performed to detect infections and to assess the amount of pressure from the cerebrospinal fluid on the brain.
- Craniography – determines the size of the newborn's head and reveals suture divergence. If the head grows more than 1.5 cm per month, this indicates hydrocephalus.
To make a final diagnosis, not only the results of the diagnostics are taken into account, but also the presence of disease symptoms. Based on the data obtained, the doctor makes a treatment plan. The earlier the therapy is started, the better the prognosis for recovery.
 [ 30 ], [ 31 ], [ 32 ], [ 33 ], [ 34 ]
[ 30 ], [ 31 ], [ 32 ], [ 33 ], [ 34 ]
Tests
Laboratory diagnostics of increased accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid system of the brain is necessary both for diagnosis and for monitoring the effectiveness of treatment. Tests for suspected hydrocele in newborns consist of:
- General and biochemical blood analysis.
- General urine analysis.
- Alanine aminotransferase.
- Analysis of feces for dysbacteriosis and occult blood.
- Analysis for intrauterine infections.
- Liquorodynamic tests.
Morphological symptoms of the disease depend entirely on the cause that provoked it and on the duration of increased intracranial pressure. The results of laboratory diagnostics are taken into account when drawing up a treatment plan.
 [ 35 ], [ 36 ], [ 37 ], [ 38 ]
[ 35 ], [ 36 ], [ 37 ], [ 38 ]
Instrumental diagnostics
The difficulty in identifying hydrocele in newborns is that children do not yet have the ability to talk about pain and other characteristics of the disease.
In newborns, diagnostics are carried out using the following instrumental methods:
- Ultrasound examination is a study of the condition of the brain through the fontanelle.
- Lumbar puncture.
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
- Neurosonography.
- Radiography.
- Ophthalmoscopy.
Instrumental diagnostics allows to detect signs of disorder already during intrauterine development of the fetus. For this purpose, an analysis of amniotic fluid and the umbilical cord of the fetus is carried out.
What do need to examine?
Differential diagnosis
As a rule, the diagnosis of hydrocephalus does not cause difficulties. Hydrocephalus is differentiated from diseases that are similar in symptoms, but are not associated with abnormal absorption of cerebrospinal fluid:
- Atrophy (hydrocephalus ex vacuo) – with this pathology there are no disturbances in cerebrospinal fluid dynamics, and there is no loss of brain matter.
- Developmental pathologies in which the ventricles are enlarged include agenesis of the corpus callosum and septo-optic dysplasia.
Differential diagnostics are performed with family cases of megalocephaly and large-headedness. In addition to standard studies, special attention is paid to radiography and diaphanoscopy (reveals an increase in the luminescence zone).
Who to contact?
Treatment of cerebral hydrocele in newborns
There are several methods to eliminate intracranial pathology associated with abnormal production of cerebrospinal fluid. Treatment of hydrocephalus in newborns can be both conservative and surgical. To ensure a good prognosis, a neurologist in a team with a neurosurgeon develops a treatment plan.
- Drug treatment of hydrocephalus
To normalize intracranial pressure, it is necessary to reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid or speed up the process of its removal. For this purpose, drugs are used that block the enzymes responsible for the secretion of cerebrospinal fluid and increase the volume of urination. Such drugs are taken simultaneously with potassium preparations, since this substance is washed out of the body.
Particular attention is paid to diuretics, which also help remove excess fluid. In addition, medications are used to improve the functioning of neurons with increased intracranial pressure. If there is no improvement in the patient's condition within 2-3 months after the start of conservative therapy, then surgical intervention is resorted to.
- Surgical treatment of dropsy
In most cases, surgery is the only way to stop the progression of the pathology, normalize intracranial pressure and save the brain. The method of surgical intervention depends on the form and stage of hydrocephalus.
If the pathology has a closed form, then this indicates an obstacle (tumor, cyst, vessel aneurysm, hematoma) that prevents the cerebrospinal fluid from circulating normally. The operation is aimed at its elimination. If tumor neoplasms have grown into the brain or they do not have clear boundaries, then surgical treatment is aimed at creating a path for the removal of cerebrospinal fluid. For this, bypass is performed.
In the case of open hydrocephalus, i.e. when the fluid is not absorbed where it is needed, shunting is performed: ventriculoperitoneal, ventriculoatrial, lumboperitoneal. Interventions aimed at normalizing the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid can also be performed, for example, dissection of arachnoid adhesions. When the synthesis of cerebrospinal fluid increases, operations are performed to stop this process. This can be the installation of clamps on the vascular plexuses of the ventricles or coagulation of these structures.
The method of treatment is determined by the doctor, individually for each patient. For this purpose, a set of various diagnostic measures is carried out, which determine the type and severity of the disease.
Medicines
Conservative treatment of hydrocephalus in a newborn is carried out to relieve painful symptoms and prevent complications of the pathological condition. Medicines are also prescribed to eliminate the consequences of the disease, for example, epilepsy or oligophrenia. Before prescribing any medication, the doctor conducts a thorough diagnosis of the baby's condition.
The following medications can be used to treat a newborn:
- Veroshpiron is an antagonist of the hormone produced by the adrenal cortex. It has a pronounced diuretic effect. It does not affect renal circulation and renal tubule function. It does not cause acid-base imbalance. It is available in tablet form.
- Indications for use: swelling caused by cardiovascular failure, diseases with fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, impaired movement of the limbs due to delayed release of potassium ions by the body.
- The method of administration and dosage are selected by the attending physician, individually for each patient. As a rule, the drug is taken 50 mg 3 times a day.
- Side effects: dizziness, increased drowsiness, hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, allergic skin reactions.
- Contraindications: severe renal failure, hyperkalemia, first trimester of pregnancy.
- Mexiprim is an antioxidant with an inhibitory effect on free radical reactions. It has membrane-protective activity. Reduces the risk of hypoxia and oxidative stress, has nootropic properties. Affects processes in cerebral cells, has an anticonvulsant, anxiolytic effect. Available in the form of tablets and injection solution.
- Indications for use depend on the form of release of the drug. Tablets are prescribed for cognitive disorders, vegetative-vascular dystonia, alcohol withdrawal, anxiety states against the background of neuroses. Injections are indicated for acute cerebral circulatory disorders, neurocirculatory dystonia, cognitive disorders against the background of atherosclerosis, discirculatory encephalopathy, and acute purulent-inflammatory pathologies of the abdominal cavity.
- Method of administration: tablets are taken orally, a single dose is 250-400 mg, the maximum daily dose is 800 mg. The course of treatment is determined by the attending physician. The injection solution is used for intramuscular and intravenous administration. The initial dosage is 50-450 mg with a gradual increase until the desired therapeutic effect is achieved.
- Side effects: nausea, drowsiness, impaired coordination of movements, headaches, allergic reactions, dry mouth, increased anxiety, hypotension, hypertension, emotional reactivity.
- Contraindications: acute liver dysfunction, lactation, intolerance to the active components of the drug, pregnancy, severe kidney dysfunction.
- Overdose causes increased drowsiness, which goes away on its own after stopping use of the medication.
- Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic. It reduces intraocular and intracranial pressure, accelerates the process of excretion of water and sodium by the kidneys. It does not affect the level of potassium ions in the blood plasma. It is available as an infusion solution.
- Indications for use: cerebral edema, increased intraocular and/or intracranial pressure, oliguria, accelerated diuresis. The drug is used for complications associated with the introduction of incompatible blood, as well as to prevent renal ischemia, hemoglobinemia and hemolysis during surgical interventions with extracorporeal circulation.
- Method of administration: the drug is used parenterally. The solution is administered by infusion drip or slowly by jet. The dosage is calculated at 500-1000 mg/kg of the patient's body weight. The duration of therapy depends on the results of treatment in the first days of drug use.
- Side effects: various dyspeptic phenomena, dryness of the oral mucosa, nausea, vomiting, arterial hypotension, tachycardia, electrolyte imbalance, allergic skin reactions.
- Contraindications: individual hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, severe forms of kidney damage, chronic heart failure, water-electrolyte imbalance, pregnancy and lactation.
- Overdose occurs when high doses of the drug are used and when it is administered too quickly. It manifests itself as increased intraocular and intracranial pressure, increased extracellular fluid, and disturbances in water-electrolyte balance.
- Diacarb is a saluretic, causes diuresis by removing certain electrolytes without disturbing the electrolyte balance in the body. It is available in tablet form.
- Indications for use: sodium and water retention in the body. Edema due to circulatory failure, liver cirrhosis and renal failure, pulmonary-cardiac syndrome. Edema caused by glaucoma, increased intracranial or intraocular pressure, tetany, epilepsy, gout.
- Method of administration: the medicine is taken orally at 125-250 mg 1-2 times a day for 2 days. The duration of therapy should not exceed 5 days.
- Side effects: drowsiness, increased fatigue, headaches, disorientation, leukopenia, hemolytic anemia. Overdose is manifested by the same side effects. Symptomatic therapy is indicated to eliminate them.
- Contraindications: acidosis, Addison's disease, hypochloremia, hypochloruria, hypokalemia, diabetes. Not used during pregnancy and simultaneously with ammonium chloride, which can cause acidosis.
- Vasobral is a combination drug. Contains azobral dihydroergocryptine, a dihydrated derivative of ergot that blocks alpha1 and alpha2 adrenergic receptors of smooth muscle cells and platelets. Stimulates dopaminergic and serotonergic receptors of the central nervous system. Reduces platelet and red blood cell aggregation. Reduces vascular permeability, improves blood circulation and metabolism in the brain. Increases the resistance of brain tissue to hypoxia. Available as a solution and tablets for oral administration.
- Indications for use: cerebrovascular insufficiency, cerebrovascular accidents, decreased mental activity, memory impairment, decreased attention, orientation disorders, migraine, cochleovestibular disorders of ischemic genesis, retinopathy, Raynaud's disease, chronic venous insufficiency. The drug is not prescribed in case of hypersensitivity to its components.
- Directions for use: 1-2 capsules or 2-4 ml 2 times a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician.
- Side effects: nausea, epigastric pain, skin allergic reactions, arterial hypotension, fainting.
- Asparkam is a source of potassium and magnesium. It is used to restore electrolyte balance. It regulates metabolic processes and has antiarrhythmic properties. It promotes the penetration of potassium and magnesium into the intracellular space and stimulates intercellular phosphate synthesis. It is available in ampoules with an infusion solution.
- Indications for use: hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, chronic circulatory failure, ischemic heart disease, heart rhythm disturbances, intolerance or toxic effects of digitalis preparations, ventricular extrasystole, paroxysms of atrial fibrillation.
- Method of administration: the drug is administered intravenously by drip or intravenously by jet. The dosage and duration of therapy depend on the severity of the disease, the patient's age and the instructions of the attending physician.
- Side effects: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, ulceration of the gastrointestinal mucosa, flatulence, venous thrombosis, dizziness, increased sweating, paresthesia, bradycardia, allergic skin reactions.
- Overdose manifests itself as hyperkalemia. To eliminate it, intravenous administration of NaCl solution or 300-500 ml of 5% dextrose solution (with 10-20 U of insulin per 1 l) is indicated. If necessary, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are possible.
- Contraindications: severe forms of myasthenia, hyperkalemia, renal failure, impaired atrioventricular conduction.
- Actovegin – activates cellular metabolism by increasing the transport and accumulation of glucose and oxygen. Improves blood supply. It has several forms of release: dragee forte, injection and infusion solution, cream, ointment and eye gel.
- Indications for use: cerebral circulatory failure, ischemic stroke, peripheral circulatory disorders, trophic disorders, ulcers and bedsores, burns, prevention and treatment of radiation injuries. The drug is effective in case of damage to the cornea and sclera. The method of administration and dosage depend on the severity of the disease and the age of the patient.
- Side effects: allergic skin reactions, increased sweating, fever, itching and burning at the site of application or injection of the drug.
- Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, pregnancy and lactation.
- Cavinton - dilates blood vessels in the brain, improves blood flow and oxygen supply to the brain. Reduces platelet aggregation, enhances the metabolism of norepinephrine and serotonin in brain tissue, reduces pathologically increased blood viscosity. Available as a 2% solution in ampoules and tablets for oral administration.
- Indications for use: neurological and mental disorders caused by cerebral circulation disorders, hypertension, vasovegetative symptoms, memory disorders, speech disorders, dizziness. The drug is used in ophthalmological practice and for hearing loss.
- Method of administration: 1-2 tablets 3 times a day for a long period of time. Improvement is observed after 1-2 weeks of regular use of the drug. Intravenous administration is indicated for neurological disorders of cerebral circulation. Initial dosage is 10-20 mg. The course of treatment is 1-2 months.
- Side effects: increased heart rate and decreased blood pressure.
- Contraindications: severe ischemic heart disease, pregnancy, unstable blood pressure and low vascular tone. The drug is prohibited to be administered subcutaneously.
- Pantogam is a nootropic, improves mental activity and memory. Increases the quality of metabolic processes and the body's resistance to hypoxia. It has an anticonvulsant effect, improves the condition of patients with cerebral insufficiency, hyperkinetic disorders, neuroleptic syndrome, clonic stuttering in children. It is available in tablet form.
- Indications for use: mental retardation, oligophrenia, speech delay, epilepsy, polymorphic attacks and epileptic seizures, trigeminal neuralgia. Subcortical hyperkinesis caused by taking neuroleptic drugs.
- Method of administration: the medicine is taken orally 15-30 minutes after meals. The recommended dosage is 500 mg 4-6 times a day, the course of treatment is 2-3 months.
- Side effects manifest themselves in the form of various allergic reactions. If they occur, discontinuation of the drug is indicated.
All medications used to treat hydrocephalus in children should be prescribed by the attending physician. During therapy, careful monitoring of the baby's condition and treatment progress is indicated.
Vitamins
In combination with drug therapy, as well as before and after surgery, patients are prescribed vitamins that improve metabolic processes in brain cells.
Let's look at the main ones:
- B vitamins – B1 improves coordination of movements and reduces fatigue. B2 speeds up mental reactions, relieves headaches and drowsiness. B3 is responsible for the level of concentration, the speed of memory recovery. B5 is involved in the transmission of impulses between nerve cells in the brain. B6 increases intelligence and improves thought processes. B9 fights increased fatigue, insomnia and apathy. B12 regulates sleep and wakefulness patterns.
- Vitamin C – ascorbic acid has antioxidant properties, protects the body from increased emotional or physical stress.
- Vitamin D – calciferol acts as a preventive measure against oncological brain damage. Maintains the elasticity of capillary walls and large vessels, prevents oxidative processes.
- Vitamin E – strengthens the walls of blood vessels in the brain, preventing their destruction.
- Vitamin P – a bioflavonoid prevents cerebral hemorrhages and capillary fragility.
Vitamins are selected by a doctor, separately for each case of hydrocephalus and each patient individually.
Physiotherapy treatment
Additional methods of treating hydrocephalus include physiotherapy. Most often, patients are prescribed:
- Microcurrent reflexology.
- Massage.
- Electrophoresis.
- Acupuncture.
- Manual therapy.
- Physiotherapy exercises.
Physiotherapy is performed at the stage when the main treatment has been successfully completed and it is necessary to restore the body. Physiotherapy procedures are prescribed to accelerate the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and to improve the psychological state and development of patients.
Folk remedies
Hydrocephalus in newborns is not a new disease. Folk treatment of this pathology has been used for a very long time. Infusions and medicinal decoctions are most often used for therapy. Let's consider folk remedies for hydrocephalus:
- Grapes - you can eat them raw, or you can make juices and compotes from them.
- A decoction of elderberry - the rhizomes and bark of the plant must be poured with boiling water, boiled, strained and filtered. This remedy is effective in the early stages of the disease.
- Onion and pumpkin juice - for medicinal purposes, take 1-2 spoons on an empty stomach.
- Infusion of parsley root.
- A decoction of lemon balm or birch leaves, calamus.
Folk treatment is not an alternative to medication or surgery. Before using this method, you must consult with your doctor and assess all the risks of such therapy.
Herbal treatment
Another alternative medicine option is herbal treatment. In case of cerebrospinal fluid production/outflow disorders, the following recipes are recommended:
- Take 20 g of peppermint and 200 ml of boiling water. Pour the plant and let it brew for 30 minutes. After cooling, strain and take as tea, but without additives and sweeteners 3 times a day.
- Pour 1 liter of boiling water over 2 spoons of cornflower flowers. Once the infusion has cooled, strain it. Take 50 ml 3 times a day. Cornflower infusion helps remove excess fluid from the body.
- Pour a glass of boiling water over a tablespoon of astragalus and let it brew for 3 hours in a dark place. Strain and take 50 ml 2-3 times a day.
- Pour alcohol over the black elderberry root in a 1:10 ratio. Let the mixture sit for a week. Take 25 drops 3 times a day.
- Grind buckthorn berries to a powder. Use the powder to prepare a medicinal drink. The remedy is taken up to 3 times a day, but the daily dose should not exceed 5 g of powder.
Before using herbal remedies to treat hydrocephalus, especially in children, you should consult with your doctor.
Homeopathy
In some cases, even with the most serious diseases, they resort to using alternative treatment methods. Homeopathy for hydrocephalus in newborns recommends the following drugs:
- Natrum sulphuricum (Aconl, Arn2, Belli, Hell, Hyper2, Nat-sl, Sill) – hydrocephalus caused by trauma.
- Helleborus niger – the disease is accompanied by severe convulsions, strabismus or other visual impairments.
- Mercurius – attacks of insomnia, anxiety, lethargy.
- Secale cornutum – loss of coordination of movements, sudden loss of body weight.
- Apis – severe headaches, the child often throws his head back, little urine comes out when urinating.
- Apocynum cannabinum – cranial sutures and fontanelle are wide open, increased intracranial pressure.
- Sulphur – pupils react poorly to light, painful sensations intensify at night.
- Glonoin - abnormal enlargement of the skull, vomiting of cerebral origin.
All of the above medications can only be used as prescribed by a homeopathic physician, who will assess all the risks of this therapy for the baby and select the necessary dosage of medications.
Surgical treatment
In most cases, surgical treatment of hydrocephalus is the only way to stop the pathological growth of intracranial pressure and save the brain. The method of surgical intervention depends entirely on the form and stage of the disease. The main objective of the operation is to drain cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles of the brain to other cavities of the body.
- Closed hydrocephalus
The type of surgical intervention in this case depends on the cause of the disorder.
- If the failure in the production and drainage of cerebrospinal fluid is associated with the presence of a tumor, cyst or hematoma, the doctor removes the pathological tissue. This normalizes the flow and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid.
- If tumors have grown into the brain and do not have clear boundaries, then shunting is indicated. During the operation, the doctor creates a path for the movement of cerebrospinal fluid, which will bypass the blockage.
Most often, cerebrospinal fluid is drained using silicone catheters into the abdominal cavity, which has increased absorption capacity. This type of surgery is called ventriculoperitoneal shunting. It is performed on more than 200,000 newborns each year.
With ventriculo-atrial shunting, the cerebrospinal fluid is diverted into the right atrium. Endoscopic ventriculostomy is also possible, which is most effective in occlusive forms of hydrocele. If the pressure in the skull increases very quickly and shunting is dangerous, then external ventricular drainage is performed. A catheter is inserted into the ventricle of the brain, with the help of which the cerebrospinal fluid is diverted.
- Open hydrocephalus
If the cerebrospinal fluid is not absorbed where it should be, then the following types of surgery are indicated:
- Ventriculo-peritoneal shunt.
- Ventriculoatrial shunting.
- Lumboperitoneal shunting.
Surgical interventions that activate cerebrospinal fluid absorption are possible, for example, dissection of arachnoid adhesions. If increased fluid synthesis is observed, the operation is aimed at suppressing the process. For this purpose, clamps can be placed on the vascular plexuses of the ventricles or the structures lining the ventricular wall can be cauterized.
If surgical treatment is successful, the progression of the pathology stops. The child returns to normal life, develops on par with peers. In some cases, surgery for hydrocele is not performed. For example, when intracranial pressure does not increase, and there are no obvious signs of disease progression. In this case, the child should be regularly monitored by a neurologist and neurosurgeon. It is necessary to systematically measure the head circumference, conduct neurosonography and CT. Medication may be prescribed with drugs that reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of having a child with hydrocephalus, future parents should carefully approach the pregnancy planning stage. Prevention begins with a consultation with a geneticist and genetic testing of both the woman and the man. The expectant mother should carefully monitor her health, avoid overwork, stress and injuries. Both before and after conception, you should lead a healthy lifestyle, protect yourself from possible infections.
During pregnancy, it is strictly forbidden to smoke, drink alcohol or take drugs. You cannot take any medications without a doctor's permission. If a woman's professional activity is associated with dangerous conditions or toxic substances, then it should be suspended for the duration of pregnancy. It is recommended to spend more time outdoors, maintain a balanced diet and get more positive emotions.
Regular check-ups and routine diagnostic tests, a healthy lifestyle and compliance with all medical prescriptions can help to minimize the risk of having a child with VGM.
 [ 41 ]
[ 41 ]
Forecast
How and how long a newborn with hydrocephalus will live depends entirely on the cause of the disease, its form, stage, and severity. The prognosis is based on factors such as:
- Presence of concomitant diseases.
- Relevance and effectiveness of the chosen treatment method.
- The degree of progression of hydrocephalus (late stages are difficult to treat and cause many pathological complications).
- Timeliness of disease diagnosis (time interval from the moment the disorder occurs to the start of treatment).
It is very important to start immediate treatment when dropsy is detected. Early stages are more amenable to therapy and allow avoiding complications, which cannot be said about advanced cases. Many patients, having undergone full treatment, do not experience health problems and forget about their diagnosis.
According to medical statistics, more than 90% of newborns with hydrocephalus successfully recover from the disease and its consequences. In 10% of cases, there is a risk of developing life-threatening conditions:
- Delays in physical and mental development (speech problems, difficulties expressing emotions).
- Constant headaches due to increased intracranial pressure.
- Deterioration of vision and complete blindness.
- Epilepsy, cerebral palsy.
- Increased nervous excitability.
- Severe sleep disturbances.
- Aggression.
- Stuttering.
- Strabismus.
- Hysteria.
- Various neuropathic disorders.
Hydrocephalus in newborns of communicating form has a more favorable prognosis. Congenital and timely diagnosed disease proceeds much easier than acquired. If treatment is started on time and correctly composed, then the baby's life continues, but there is a risk of deterioration of its quality (speech, vision, hearing, coordination of movements disorders).

