
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Cervical dysplasia after childbirth
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 08.07.2025
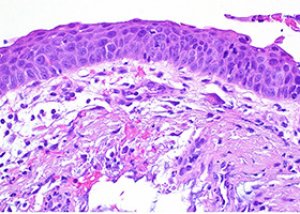
Cervical dysplasia (CIN) cannot be a contraindication to pregnancy and bearing a child. The course of dysplasia does not affect the fetus due to its good placental protection. Just as the pregnancy process does not provoke a worsening of the symptoms of CIN and almost never leads to degeneration into an oncological process. Moreover, hormonal changes in the female body bearing a child can give a false clinical picture, very similar to the signs of cervical dysplasia in the initial stages. Pseudo-erosion looks like inflammation of the cervix during examination, but this is due to physiological changes in the epithelium, when the cervical cells are forced to move closer to the vagina. Such temporary "transportation" of cell layers is considered normal.
Any sign of a pathological process that worries a woman or a doctor is often associated with manifestations of a secondary infection - HPV, chlamydia, colpitis, etc. To clarify the factor that provokes symptoms, an epithelial tissue sample is taken (PAP test), a smear is taken for the state of the microflora. If the result of laboratory tests is positive, after the birth of the child the woman needs a follow-up examination, a comprehensive examination and treatment.
Cervical dysplasia during pregnancy of the third stage as an oncological process is also not considered a direct contraindication to bearing a child, however, the gynecologist agrees on the tactics of pregnancy management together with a specialist - an oncologist.
Cervical dysplasia after childbirth
CIN (cervical dysplasia) does not determine the woman’s condition – before or after childbirth; this disease occurs with equal frequency.
The characteristic stages of the course, which are characteristic of cervical dysplasia, do not change during pregnancy, just as they cannot accelerate or slow down after childbirth. An exception can be considered the third stage, when CIN turns into the initial form of cancer. There are also statistics from foreign research institutes, which claim that after childbirth the dysplasia process can change:
- Disease regression (cell transformation stops and subsides) - 25-30%
- Cervical dysplasia remains in a stable stage – 40-45%
- Disease progression in grade III CIN – 15-20%
To relieve the anxiety of young mothers, it is worth noting the following points:
- Cervical dysplasia cannot be a direct indication of cancer; most often, the first two stages are successfully treated provided that a comprehensive examination and regular monitoring by a doctor are completed
- Cervical cancer, grade III cervical dysplasia after childbirth is diagnosed very rarely – 10-12 women per 100,000 cases of pregnancy and childbirth. The epithelial tissue of the cervix during pregnancy is characterized by a high level of protection from progesterone. In turn, hormonal transformations can cause a false picture, clinically similar to dysplasia or erosive process (ectropion)
- Cervical dysplasia after childbirth does not require additional cytology if the woman underwent regular examinations and screening of the epithelial tissue condition before pregnancy.
- After the birth of a child, the structure of the cervical epithelium may change due to natural causes (the process of childbirth). This is especially true for those mothers who breastfeed their child. Examination and preventive examinations of such women are carried out only at the end of the period of breastfeeding. The exception is diagnosed grade III dysplasia during pregnancy.
There are also peculiarities in the course of the dysplastic process after childbirth, if the diagnosed disease required conization during gestation.
Removal of the cervical sector does not affect the pregnancy process. However, after childbirth, a woman should be monitored by a gynecologist to avoid relapses and, in principle, eliminate the cause of cervical dysplasia. Also, cervical dysplasia after childbirth can be associated with a difficult delivery - ruptures of the epithelial tissue. Ectropion (eversion of the cervix) is treated only surgically and never goes away on its own. A secondary process can join it, which together gives a clinical picture similar to dysplasia of the 2nd or even 3rd degree. Traumatic injuries in the presence of a hidden, undiagnosed and untreated infection are the path to dysplastic processes, and, therefore, to precancerous pathology. And vice versa, timely examination after childbirth, the identification of temporary or previously undiagnosed pathologies help to avoid the risk of developing cervical cancer.
 [ 6 ]
[ 6 ]
Who to contact?

