
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Basilar artery thrombosis.
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 12.07.2025
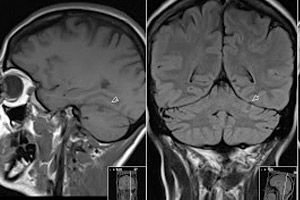
In modern conditions, pathologies and diseases associated with disruption of the normal functioning of the heart and blood vessels are increasingly observed. Various pathologies of the vascular bed are ranked third in the overall human morbidity system. Due to poor nutrition, constant stress, and negative environmental factors, the risk of blood clots is currently increasing sharply.
Thrombosis is the formation of a thrombus (blood clot) in the lumen of a blood vessel. Arterial thromboses are the most dangerous. The most dangerous of all known thromboses is basilar artery thrombosis.
The basilar artery is an artery that forms in the lower part of the medulla oblongata. It ensures the full functioning of the entire brain. The basilar artery is formed at the confluence of the paired carotid arteries and the paired vertebral arteries. It is responsible for ensuring that the brain receives a sufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients. The basilar artery delivers approximately 70% of all the blood it needs to the brain. Its various lesions, including basilar artery thrombosis, can be fatal. Thrombosis of the basilar artery can result in a stroke, which is often fatal.
 [ 1 ]
[ 1 ]
Epidemiology
Basilar artery thrombosis is defined as a syndrome. This syndrome is most often a concomitant disease with osteochondrosis: every third person develops thrombosis.
It occurs in both adults and children. Elderly people suffer from this syndrome 3 times more often than adults, and 4.5 times more often than adolescents and children. In old and senile age, approximately 60% of cases end in disability, 10% in death. Whereas in childhood, these figures are 15% and 1.5%, respectively. Basilar artery thrombosis often occurs in combination with diseases such as:
- embolism in the vertebrobasilar zone – 21%;
- arrhythmia combined with thrombosis in other parts of the body – 25%;
- atherosclerosis – 21%;
- presence of blood clots in the lower extremities – 16%;
- arterial compression – 6%;
- severe blood thickening, platelet dysfunction – 7%
- other pathologies – 4%.
Causes basilar artery thrombosis.
The main cause of basilar artery thrombosis is the formation of a thrombus in the wall of the basilar artery. The following may be the causes of basilar artery thrombosis:
- Congenital pathologies, such as abnormal structure of the walls of blood vessels, impaired vascular tone. Also, the process of thrombus formation is facilitated by such pathologies as Kimmerpy anomaly, various hypoplasias, dystonic changes;
- Congenital anatomical features of the arteries (abnormal tortuosity of the vertebral and basilar arteries, insufficient number of anastomoses at the base of the brain);
- Injuries of various nature (sports, domestic, road traffic). First of all, the danger is posed by traumatic impacts, traumatic injuries in the neck-collar zone, the back of the head;
- Inflammatory processes in the walls of blood vessels;
- Arterial stenosis resulting in thrombus formation;
- Atherosclerotic disease of blood vessels;
- Microangiopathy, which is a consequence of various diseases;
- Antiphospholipid syndrome, accompanied by a violation of the vascular lumen;
- Disruption of the biochemical cycle and hormonal background;
- Compressive disorders resulting from hypertrophy of the scalene muscle and hyperplasia of the cervical vertebrae;
- Compression of the basilar artery or vertebral artery by hernia, spondylosis and other concomitant pathologies;
- Antiphospholipid syndrome, accompanied by obstruction of blood vessels;
- Disruption of the biochemical cycle and hormonal background.
Risk factors
The likelihood of developing basilar artery thrombosis increases in the presence of the following risk factors:
- Improper nutrition, leading to the deposition of cholesterol plaques. Excessive consumption of food containing fat, oil, cholesterol. Fast food, lack of a diet;
- Genetic predisposition to thrombosis;
- Disorders of the basic properties of blood;
- Blood microcirculation disorders;
- Cardiogenic embolism, small arterial embolism
- Complete occlusion of the lumen of a blood vessel resulting from atherosclerotic stenosis.
- Staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of basilar artery thrombosis is based on a reversible disruption of the basilar artery function and its conductivity, which occurs as a result of thrombus formation processes in the arterial thickness.
As a consequence, the functional state of the brain is disrupted, which is associated with a disruption of blood circulation in the area fed by the main and vertebral arteries. Neurological symptoms develop. Acute cerebral ischemia is observed.
The severity of the disease and the degree of expression of symptoms depend on the location of the pathological process and its size, as well as on the possibility of collateral circulation.
Symptoms basilar artery thrombosis.
The diagnosis of basilar artery thrombosis is based on a symptom complex that includes the following disorders:
- visual disturbances (loss of visual field, agnosia, blindness, photopsia, blurred vision, appearance of visual images);
- disorders of eye motor functions;
- disorders of the vestibular apparatus;
- pathology of the pharyngeal and laryngeal function (a person may feel discomfort in the throat area, may be bothered by a feeling of a “lump” in the throat, a sore throat, spasms and difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, cough);
- vegetative disorders: nausea, vomiting;
- sensory (sensitivity) disorders, skin lesions;
- movement disorders (paresis, ataxia, sensory disturbances). Gait disturbances are also observed, which may be accompanied by tremors, decreased muscle tone;
- asthenic syndrome;
- psychiatric disorders.
All symptoms are conventionally divided into two categories: paroxysmal and permanent. Paroxysmal symptoms and syndromes are observed episodically, during attacks and exacerbations, and manifest themselves in an acute form. Permanent symptoms are sluggish, last for a long time, and become chronic.
First signs
If a person experiences a sharp decrease in hearing acuity, which is combined with tinnitus, one should be wary. This may be the first sign that the process of thrombus formation has begun in the basilar artery.
The appearance of audiological disorders and an increase in the intensity of noise in the ear may indicate cerebrovascular insufficiency.
In the early stages of basilar artery thrombosis, short-term hearing loss may be observed, which is combined with tinnitus. Such patients require close attention, since the situation may worsen in the future.
Since the basilar artery supplies blood to the main part of the body - the brain, pain cannot be ignored. Especially if these symptoms are constant and long-lasting, acquire a chronic and systematic character. They can also be the first signs of basilar artery thrombosis.
Stages
Basilar stage thrombosis develops in several stages. The first stage is the initial one. At this stage, precursors appear or thrombosis first manifests itself against the background of general weakness, pain symptoms in the occipital region. At this stage, it is important to promptly and correctly diagnose thrombosis, prescribe the correct therapy, then a favorable prognosis is possible. Outpatient treatment is possible.
The second stage is thrombus formation. At this stage, a thrombus forms in the lumen of the basilar artery, the lumen of the artery narrows, and the blood supply to the brain is disrupted. The condition worsens. Hospitalization and inpatient treatment are necessary. Constant monitoring by a doctor is necessary to prevent a stroke, and complex treatment.
The third stage is the stage at which the thrombus is quite pronounced and disrupts normal brain function. If treatment is incorrect and untimely, complications such as stroke, serious consequences, including disability and death, are possible. At this stage, the help of a neurosurgeon is required, which consists of thrombectomy and restoration of cerebral blood flow.
The outcome of therapy depends on the timeliness of diagnosis, correct treatment, and properly selected rehabilitation measures.
Forms
Basilar artery thrombosis is a diagnosis. In ICD-10 it is characterized as a syndrome, not a disease, and is one of the subtypes of general thrombosis.
Basilar artery thrombosis may manifest itself in the following syndromes:
- Wallenberg-Zakharchenko syndrome (occurs as a result of damage to the lower back of the brain);
- Dejerine and Millard-Gubler syndrome (the medial branches of the bronchial artery are affected by thrombosis);
- Jackson syndrome - occurs as a result of damage to the anterior zone of the basilar artery;
- Benedict's and Weber's syndromes, in which the posterior cerebral arteries and interpeduncular branches of the basilar artery are affected.
 [ 22 ]
[ 22 ]
Complications and consequences
Basilar artery thrombosis is dangerous because it can have serious consequences and complications, which quite often have a fatal outcome.
Since the disease is associated with the formation of a thrombus in the basilar artery, its main danger is that it can break off and completely block the vessel.
In this case, a stroke occurs. A common complication is ischemic stroke of the brain, which occurs in the vertebrobasilar basin. This pathology entails disability.
The consequences of a stroke may be a systematic circulatory disorder, dizziness, complete or partial limitation of the ability to move the eyes, weakening of the eye muscle, nystagmus of the eyeballs. A common disorder is strabismus. Often a person is unable to walk straight, control their movements in space. The patient moves like a drunk, and there may be tremors, paralysis of the whole body or individual body segments, loss of sensitivity.
The consequences of a stroke can also include mental retardation, isolation, lack of socialization, difficulties in communication and learning, constant headaches, migraines. In some cases, there can be a fatal outcome.
Diagnostics basilar artery thrombosis.
It can be quite difficult to diagnose basilar artery thrombosis. Firstly, this disease can have many objective and subjective symptoms. Secondly, this diagnosis must be made in a timely manner. Thirdly, the disease must be differentiated from a number of other diseases that have similar symptoms. Therefore, it is strictly forbidden to diagnose and self-medicate on your own. As soon as you begin to be bothered by early symptoms that could indicate basilar artery thrombosis, you should consult a neurologist.
Instrumental diagnostics
When diagnosing a disease, it is important to know the cause of the disease. For this, instrumental methods are used and laboratory tests are conducted.
The following methods are used for diagnostics:
- ultrasound Dopplerography. This method makes it possible to determine occlusions, blood flow velocity, and features of blood flow movement in the arteries of the vertebrobasilar basin;
- angiography, which can be used to study the characteristics of arterial walls;
- X-ray of the spine, which allows to assess the general condition of blood flow and arteries;
- with the use of computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), it became possible to evaluate blood flow and identify various pathologies;
- infrared thermography, which is used to assess the condition of individual organs and systems based on the analysis of thermal radiation;
- rheoencephalography, which allows one to evaluate the characteristics of the blood supply to the brain;
- MR angiography, which is used to study the vascular bed.
Tests for basilar artery thrombosis
The main type of laboratory research is a blood test for biochemistry, which allows tracking changes in the biochemical cycle and identifying inflammatory processes. The study of the coagulating properties of blood and the study of its biochemical composition can be significant. It is important to evaluate such indicators as glucose and lipid levels.
Important information can also be obtained by testing blood clotting.
Differential diagnosis
Thrombosis of the basilar artery must be differentiated from a number of other pathologies that have similar features. First of all, it must be differentiated from ordinary benign paroxysmal dizziness, which may not be caused by a thrombus, but by ordinary damage to the vestibular apparatus of various etiologies. As a rule, these lesions are not associated with circulatory disorders. A reliable test that allows one to distinguish thrombosis from damage to the vestibular apparatus is the Hallpike test.
It is also necessary to refute the presence of vestibular neuronitis, acute labyrinthitis, Meniere's disease, hydrolabyrinthitis, which in most cases are complications of chronic otitis.
After this, it is differentiated from perilymphatic fistula, which occurs as a consequence of trauma or surgery. Basilar artery thrombosis can often be confused with acoustic neuroma, demyelinating diseases, and normative hydrocephalus, which is a complex of cognitive disorders.
In some cases, it is necessary to differentiate from emotional and mental disorders that manifest themselves in the form of anxiety, depressive states. Some similarities with thrombosis in various pathologies of a degenerative and traumatic nature, hearing disorders, tinnitus may also be observed.
When making a diagnosis, the doctor must take into account that similar disorders also occur in elderly people. About a third of the elderly population notes systematic tinnitus. Moreover, most patients claim that they feel high-intensity noise. These sensations, as a rule, cause great inconvenience.
Cerebrovascular pathology can result in various auditory disorders. These processes occur in most cases in the middle ear. Short-term episodes of hearing loss may be observed, which may be combined with tinnitus.
Who to contact?
Treatment basilar artery thrombosis.
Treatment of thrombosis can be outpatient and inpatient. Outpatient treatment can be given to a person at the initial stages of thrombosis, in cases where early symptoms appear or their manifestation has not even begun. In the acute or advanced phase, a person is necessarily hospitalized, since he requires constant observation and control by medical personnel. The main purpose of hospitalization is to prevent strokes. This form of treatment is called inpatient.
Usually, complex therapy is used - medications, physiotherapy. The use of folk remedies is allowed, but it is better to consult a doctor first. Remember that thrombosis is a rather dangerous diagnosis. Even the slightest mistake or inaccuracy can cost you a lot.
Basically, treatment is determined by the cause of the disease and is selected individually for each patient. Timely and correct determination of the cause of the disease is the main factor in successful treatment.
Drug treatment usually includes the use of vasodilators. These drugs prevent occlusions. They are often used in spring and autumn. The doses are small at first, then gradually increased.
Antiplatelet agents are also prescribed - drugs that turn blood into a more liquid fraction, thanks to which its coagulability is significantly reduced, which in turn prevents the formation of blood clots. Metabolic and nootropic drugs that improve functional processes in the brain are included in the complex therapy. If necessary, antihypertensive drugs can be prescribed.
It is recommended to use drugs that have a systematic effect. Painkillers (if needed), sleeping pills, antidepressants are used. If necessary, anti-dizziness drugs and antiemetics are prescribed.
Medicines used for basilar artery thrombosis
First of all, drugs are needed that will make the brain function fully, using its functional and energy reserves to the maximum. They will eliminate symptoms and relieve pain. The drugs are relatively safe and require long-term use. The main precaution is to follow the dosage and regimen. It is recommended to consult a doctor, especially if the use of these drugs is combined with other drugs and procedures. Side effects and cases of overdose are rare. In some cases, the patient may feel dizzy, nauseous, and have ringing in the ears. Sometimes there is a clouding of consciousness.
It is recommended to use the drug Nicergoline. The dose depends on the patient's characteristics. On average, it is necessary to use 5-10 mg. The number of doses is three per day.
An effective drug is cinnarizine. You should start taking it with minimal concentrations - 12.5 mg in the morning, at lunchtime and in the evening. Gradually increase the dosage to 25-50 mg at a time. Take the drug after meals.
Another drug that can be recommended for basilar artery thrombosis is pyrocetam. It is recommended to use it at 0.8 g. Take the drug as soon as you wake up, during the day and before going to bed. The duration of treatment is 2 months.
Cerebrolysin can also be recommended. This drug is used 5-10 ml intravenously. The course of therapy ranges from 5-10 injections.
Vitamins recommended for thrombosis
The main vitamin recommended for use in basilar artery thrombosis is vitamin C, which has antioxidant properties. It strengthens and cleanses the walls of blood vessels, thins the blood, and prevents platelet accumulation. It is necessary to take 500-1000 mg daily. The course of treatment is 2-4 times a year, for 30-35 days.
Vitamin D. It is recommended to use in a dosage of 35-45 mcg per day. This vitamin improves blood flow, increases platelet lysis.
It is recommended to use B vitamins in a dosage of 3-4 mcg per day, the course is approximately 1 month. These vitamins strengthen the walls of blood vessels, increase blood flow, and reduce the risk of blood clots.
Surgical treatment of basilar artery thrombosis
If drug therapy and physiotherapy are ineffective, a surgical method is used. It is aimed at mechanically removing the thrombus and limiting the affected area from the general blood flow (endarterectomy). The surgical method can also be aimed at improving blood flow. A common type of surgical intervention is angioplasty, during which a special stent is inserted into the basilar artery to prevent narrowing of the arterial lumen. This helps to normalize blood circulation.
Direct and endovascular methods are used. The method is selected after a preliminary examination and is determined by the size and characteristics of the pathology, localization and severity of the pathological process, and the state of blood flow.
Postoperative treatment and patient recovery are also carried out. After the operation, the main treatment is just beginning. A long course of therapy and rehabilitation is required. Treatment, as a rule, includes the fight against cerebral edema, thrombus formation. It is also necessary to normalize the water-electrolyte balance and use various symptomatic means aimed at eliminating the symptoms.
After eliminating the main symptoms and normalizing the condition, it is necessary to use therapeutic exercise. Exercises are also selected individually. It is recommended to undergo a course of manual therapy, physiotherapy. Acupuncture has proven itself well.
Physiotherapy treatment
Physiotherapeutic methods include manual therapy, hirudotherapy, reflexology, magnetic therapy, and wearing a cervical corset. It is also useful to attend massage sessions and exercise therapy classes. One or more methods are prescribed in combination, depending on the individual course of the disease and well-being.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies can be very effective in treating basilar artery thrombosis. However, only a combination of therapy prescribed by a doctor and folk remedies can contribute to successful treatment and overcoming the disease. If in doubt, it is always better to consult a doctor.
Garlic. During thrombosis, the blood thickens (that is why a thrombus forms). Garlic thins the blood and, accordingly, thrombi form less often. Take 3 large heads of garlic, mince them or squeeze them out with a garlic press. Transfer the resulting mass to a jar and put it in a cool place. Let it brew for 3 days, strain. Add about the same amount of juice from a freshly squeezed lemon and honey to the resulting extract. Use about 15 g of the suspension (in the evening). Store this remedy in the refrigerator.
Horse chestnut. This is a remedy that helps reduce blood clotting. Take about 500 g of chestnut seeds. Do not separate from the peel. Rub. Pour 1.5 vodka. Infuse the remedy for a week, then strain. Drink about 5 g of infusion, half an hour before you start eating. Three times a day will be enough.
Hawthorn. Has vasodilating properties. Collect about 20 g of hawthorn berries, pour a glass of boiling water. Keep in a water bath for about 3 minutes. Then insist the remedy for about half an hour. Drink 15 g in the morning, at lunch, in the evening.
 [ 33 ], [ 34 ], [ 35 ], [ 36 ]
[ 33 ], [ 34 ], [ 35 ], [ 36 ]
Herbal treatment
It is recommended to use the following herbs: stinging nettle, white acacia, hazelnut, common hops.
Nettle infusion. The method of preparation is as follows: 1 tablespoon of nettle leaves + 250 ml of boiling water. Let the decoction brew for half an hour. Then strain. Drink 60-70 ml in the morning, afternoon and evening.
White acacia is used in the form of an alcohol tincture, externally. Method of preparation: 60 g of acacia flowers are poured with a glass of vodka and infused for 7 days. After that, rub into the inflamed areas of the veins and arteries of the back of the head.
Hazelnut is used in the form of an infusion. The bark and leaves are used. To prepare the infusion, 15 g of finely chopped or grated leaves and bark are poured with a glass of boiling water. Then heated to a boil. Allow to brew for an hour. Then strain. Take half a glass orally, 2 times a day.
Hop cones are used as a decoction. The cones are crushed. 15-30 g of cones are poured with 250 ml of boiling water, heated in a water bath for 15 minutes, and filtered. Drink 125 mg three times a day.
Homeopathy for basilar artery thrombosis
Homeopathic remedies for basilar artery thrombosis are used to cleanse the vessels, thin the blood, remove toxins, and prevent thrombus formation. The method is useful and relatively safe, since side effects are quite rare.
Overdose may cause nausea, vomiting, dizziness, drowsiness. Precautions - do not take without prior consultation with a doctor, in the late stages of thrombosis, after surgery (if the doctor has not included these drugs in the complex therapy).
The following remedies are recommended:
Mumiyo. It is recommended to use mumiyo internally (balm of the Central Asian mountains). Take 0.2 g orally 2 times a day before meals. Conduct 2-3 courses of 10 days. Breaks between courses are 5-10 days.
Herbal collection "Altai Bouquet". To prepare, take the following ingredients:
- Bergenia crassifolia (black leaves) – 2 parts
- Golden root - 1 part
- The Forgotten Kopeechnik – Part 1
- Leaves of common lingonberry – 1 part
- Blueberry leaves - 1 part
- Ivan tea leaves – 1 part
- Currant leaves – 1 leaf
- Mountain thyme – 0.5 parts.
To prepare 30-45 g of the substance, pour 1000 ml of boiling water, let it brew for 20-30 minutes. Drink 400-600 ml per day.
You can add honey.
Juice of Chinese magnolia vine. Take 15 g orally per glass of tea two or three times.
Bloody-red hawthorn juice. Take 30 g orally half an hour before meals, in the morning and before bed.
Prevention
Basilar artery thrombosis can be prevented, so it is necessary to follow preventive measures for this disease. To prevent thrombosis, it is necessary to follow a diet and proper nutrition. It is necessary to eat less fatty, fried foods containing cholesterol, fatty acids. You cannot eat fast food. It is necessary to eat more seafood, garlic, berries, citrus fruits. You also need to include more vegetables in your diet, especially tomatoes, sweet peppers.
You need to consume less salt.
You need to give up bad habits. Smoking and alcohol aggravate the disease.
Regular physical activity should become a habit. Physical therapy is especially useful.
Constant monitoring of blood pressure is necessary. You cannot sit in an uncomfortable position for a long time.
Swimming is also useful. You should visit the pool at least twice a week.
Periodically, it is necessary to conduct preventive examinations and preventive treatment courses.
 [ 37 ]
[ 37 ]
Forecast
The prognosis in most cases is unfavorable. It can be favorable only if all the doctor's recommendations are followed, with correct treatment, complex treatment, and timely diagnosis.
Without proper treatment, do not expect a favorable prognosis. The patient's condition will constantly worsen. Ischemic attacks may occur, which will become more frequent every day. Ultimately, a stroke and discirculatory encephalopathy develop, which end in irreversible brain damage.

