
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Ovarian resection: consequences, recovery after surgery, the possibility of getting pregnant
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
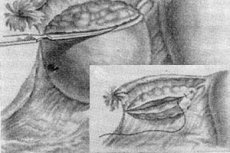
Surgical intervention is often used in gynecology when it is necessary to remove cysts, tumors, adhesions, endometriosis, etc. The most common operation is considered to be ovarian resection - this is a partial excision of damaged ovarian tissue while preserving a certain healthy area. After resection, the function of the ovary is also preserved in the vast majority of cases.
Indications for the procedure
Partial ovarian resection may be prescribed in the following situations:
- in case of a single ovarian cyst that does not respond to drug treatment, and when its size exceeds 20 mm in diameter (including dermoid cysts);
- in case of hemorrhage into the ovary;
- with purulent inflammation of the ovary;
- when a benign formation in the ovary is diagnosed (for example, cystadenoma);
- in case of mechanical damage to the ovary (including during other surgical interventions);
- in case of ectopic ovarian implantation of the embryo;
- in case of torsion or rupture of cystic formations, accompanied by bleeding and pain;
- with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Ovarian resection for polycystic disease
Polycystic disease is a rather complex hormonal disease that occurs when the hypothalamic regulation of ovarian function fails. In case of polycystic disease, the diagnosis of "infertility" is often made, so ovarian resection is one of the ways to help a woman get pregnant.
Depending on the complexity and course of the polycystic process, the following surgical interventions can be performed:
- Ovarian decortication surgery involves removing the thickened outer layer of the ovaries, i.e. cutting it off with a needle electrode. After the thickening is removed, the wall will become more flexible, and normal maturation of the follicles with normal release of the egg will occur.
- The ovarian cauterization operation consists of a circular incision of the ovarian surface: an average of 7 incisions are made to a depth of 10 mm. After this procedure, healthy tissue structures capable of developing high-quality follicles are formed in the area of the incisions.
- Wedge resection of the ovaries is an operation to remove a specific "wedge" of triangular tissue from the ovary. This allows the formed eggs to exit the ovary to meet the sperm. The effectiveness of this procedure is estimated at approximately 85-88%.
- The procedure of ovarian endothermocoagulation involves inserting a special electrode into the ovary, which burns several small holes in the tissue (usually about fifteen).
- Ovarian electrodrilling surgery is a procedure to remove cysts from the affected ovary using an electric current.
Advantages and disadvantages of laparoscopy for ovarian resection
Ovarian resection, which is performed using laparoscopy, has a number of advantages over laparotomy:
- laparoscopy is considered a less traumatic intervention;
- adhesions after laparoscopy occur rarely, and the risk of damage to nearby organs is reduced to a minimum;
- recovery of the body after laparoscopic surgery occurs many times faster and more comfortably;
- the possibility of disruption of the suture row after surgery is excluded;
- the risk of bleeding and wound infection is reduced to a minimum;
- there are virtually no post-operative scars.
The only disadvantage of laparoscopy is the relatively high cost of the surgical procedure.
Preparation
Before an intervention for ovarian resection, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics:
- donate blood for general and biochemical analysis, as well as to determine HIV and hepatitis;
- check the heart function using cardiography;
- do a fluorogram of the lungs.
Both laparotomic and laparoscopic resections are surgeries performed under general anesthesia. Therefore, when preparing for surgery, it is necessary to take into account the stage of preparation for general anesthesia. The day before the intervention, you should limit your diet, eating mainly liquid and easily digestible food. The last meal should be no later than 6 p.m., and liquid intake should be no later than 9 p.m. On the same day, you should give an enema and cleanse the intestines (the procedure can be repeated the next morning).
On the day of surgery, you are not allowed to eat or drink. You also cannot take any medications unless prescribed by your doctor.
Technique ovarian resection
The ovarian resection operation is performed under general anesthesia: the drug is administered intravenously and the patient "falls asleep" on the operating table. Then, depending on the type of operation being performed, the surgeon performs certain actions:
- Laparoscopic resection of the ovaries involves making three punctures - one in the navel area and two others in the projection area of the ovaries;
- Laparotomic ovarian resection is performed by making one relatively large tissue incision to gain access to the organs.
Next, medical instruments are inserted into the abdominal cavity, with which the surgeon performs the appropriate manipulations:
- frees the organ being operated on for resection (separates it from adhesions and other organs located nearby);
- applies a clamp to the suspensory ovarian ligament;
- performs the necessary version of ovarian resection;
- cauterizes and sutures damaged vessels;
- sutures damaged tissues with catgut;
- conducts a diagnostic examination of the reproductive organs and assesses their condition;
- if necessary, performs the elimination of other problems in the pelvic area;
- installs drains to drain fluid from the surgical wound;
- removes instruments and sutures external tissues.
In some cases, a planned laparoscopic operation may be transformed into a laparotomy operation: it all depends on what changes in the organs the surgeon sees when directly accessing them.
Resection of both ovaries
If both ovaries are removed, the operation is called an oophorectomy. It is usually performed:
- in case of malignant organ damage (in this case, resection of the uterus and ovaries is possible, when the ovaries, tubes and partially the uterus are removed);
- with large cystic formations (in women who do not plan to have more children – usually after 40-45 years);
- for glandular abscesses;
- in case of total endometriosis.
Resection of both ovaries can also be performed unscheduled - for example, if another, less severe diagnosis was made before laparoscopy. Often, the ovaries are removed from patients after the age of 40 to prevent their malignant degeneration.
The most common procedure is resection of both ovaries in bilateral endometrioid or pseudomucinous cysts. In the case of papillary cystoma, resection of the uterus and ovaries may be used, since such a tumor has a high probability of malignancy.
Partial resection of the ovary
Ovarian resection is divided into total (complete) and subtotal (partial). Partial ovarian resection is less traumatic for the organ and allows preserving normal ovarian reserve and the ability to ovulate.
Partial resection is used in most cases of single cysts, inflammatory changes and compaction of ovarian tissue, and ruptured and torsioned cysts.
This type of surgical intervention allows organs to quickly recover and resume their function.
One of the options for partial resection is wedge resection of the ovary.
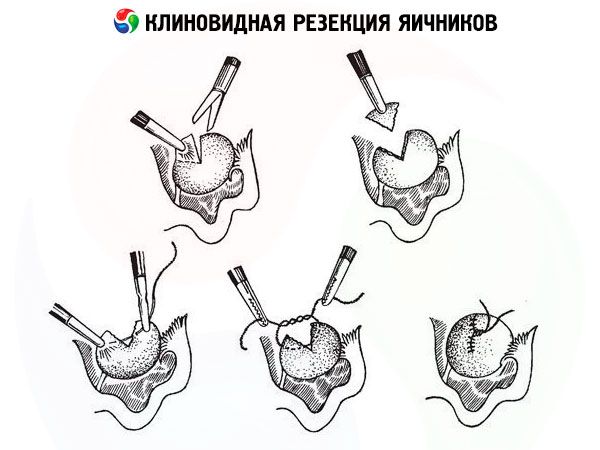
Repeat ovarian resection
A repeat operation on the ovaries may be prescribed for polycystic disease (not earlier than 6-12 months after the first resection), or if a recurrence of the cyst is detected.
Some patients have a tendency to form cysts – this predisposition may be hereditary. In such cases, cysts often recur, and it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention again. It is especially important to perform a repeat resection if a dermoid cyst larger than 20 mm is detected, or if the woman has been unable to become pregnant for a long time.
If the operation is performed for polycystic disease, then a repeat resection gives the woman additional chances to conceive a child - and it is recommended to do this within six months after the surgery.
Contraindications to the procedure
Doctors divide possible contraindications to ovarian resection into absolute and relative.
An absolute contraindication to surgery is the presence of malignant neoplasms.
Relative contraindications include urinary tract and genital infections in the acute stage, fever, blood clotting disorders, and intolerance to anesthetic medications.
Complications after the procedure
The period after partial ovarian resection surgery usually lasts about 2 weeks. After complete ovarian removal, this period is extended to 2 months.
Complications after such an operation can occur, as after any other surgical intervention:
- allergy after anesthesia;
- mechanical damage to abdominal organs;
- bleeding;
- the appearance of adhesions;
- infection getting into the wound.
In any version of ovarian resection, a part of the glandular tissue containing the reserve of eggs is removed. Their number in a woman's body is strictly defined: usually it is about five hundred such cells. Every month during ovulation, 3-5 eggs mature. Removal of a part of the tissue reduces the volume of this reserve, which depends on the volume of the resection. This leads to a reduction in the woman's reproductive period - the time during which she is able to conceive a child.
In the first period after ovarian resection, a temporary decrease in the amount of hormones in the blood is observed - this is a kind of response of the body to organ damage. Restoration of ovarian function occurs over 8-12 weeks: during this period, the doctor can prescribe supporting hormonal drugs - replacement therapy.
Menstruation after ovarian resection (in the form of spotting bloody discharge) can resume as early as 2-3 days after the intervention - this is a kind of stress reaction of the reproductive system, which in this situation is considered normal. The first postoperative cycle can be either anovulatory or normal, with ovulation. Full restoration of the menstrual cycle is observed after several weeks.
Pregnancy after ovarian resection can be planned as early as 2 months after the surgery: the monthly cycle is restored, and the woman retains the ability to conceive. If the resection was performed due to a cyst, then the best time to try to get pregnant is the first 6 months after the surgery.
Sometimes tingling sensations are observed after ovarian resection - most often they appear as a result of impaired blood circulation in the organ after surgery. Such sensations should disappear within a few days. If this does not happen, you need to visit a doctor and undergo diagnostics (for example, ultrasound).
If the resection was performed using the laparoscopy method, then during the first 3-4 days the woman may feel pain in the chest, which is associated with the peculiarities of this method. This condition is considered absolutely normal: the pain usually goes away on its own, without the use of medications.
The ovary may hurt after resection for another 1-2 weeks. After that, the pain should go away. If the ovary hurts after resection, and a month or more has passed since the operation, then you should see a doctor. The pain can be caused by the following reasons:
- inflammation in the ovary;
- adhesions after resection;
- polycystic disease.
Sometimes pain in the ovary can appear during ovulation: if such sensations are unbearable, then you should definitely see a doctor.
Care after the procedure
After the completion of the ovarian resection procedure, the patient is transferred to the postoperative ward, where she stays for 24-48 hours, depending on her condition. Getting up and walking is allowed closer to the evening or the next morning.
On the second day, the doctor may remove the installed drainage tubes, after which he will prescribe a short course of antibiotics to prevent the development of infectious complications.
After a week, the surgeon removes the stitches. The total duration of the rehabilitation period after ovarian resection is usually 14 days.
It is advisable to use compression underwear or wear a support belt for a month after the operation. During this time, it is necessary to abstain from sex and minimize physical activity.
Rehabilitation period after ovarian resection
Laparoscopic ovarian resection is the most commonly performed procedure, so let's look at the course and rules of the rehabilitation period for this type of surgical intervention.
After laparoscopic resection, it is necessary to listen to the following advice from doctors:
- sexual intercourse should not be resumed earlier than 1 month after resection (the same applies to physical activity, which is increased gradually, gradually bringing it to the usual level);
- for 12 weeks after resection, you should not lift weights greater than 3 kg;
- For 15-20 days after surgery, it is necessary to make minor adjustments to your diet, excluding spices, seasonings, salt and alcoholic beverages from your menu.
The monthly cycle after resection often recovers on its own and without any particular problems. If the cycle is disrupted, it may take two or three months, no more, to recover.
To prevent the recurrence of cysts, the doctor may prescribe preventive medications according to individual therapeutic regimens.
The body of a patient who underwent ovarian resection fully recovers after the operation within 1-2 months.
 [ 24 ]
[ 24 ]

