
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Intestinal pain
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
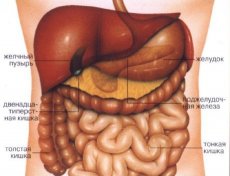
Intestinal pain is a specific feeling of discomfort, distress and pain in the abdominal area. These pains are usually associated with functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract as a result of injuries or diseases. There are important facts about this pain that everyone should know.
Possible Causes of Abdominal Pain
- Pneumonia (inflammation of the lungs)
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Pleurisy (irritation of the lining of the lungs)
- Pulmonary embolism (blood clots in the lungs)
Functional problems of the abdominal area:
- Non-ulcer dyspepsia (discomfort after eating, but not due to an ulcer, but for other reasons)
- Sphincter dysfunctions
- Problems with the bile duct valve
- Functional abdominal pain (pain in the intestines without a clear cause)
- Irritable bowel syndrome (pain associated with bowel movements)
Upper Abdominal Cancer:
- Hepatoma (liver cancer)
- Cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct problem or gallbladder cancer)
- Pancreatic cancer
- Stomach cancer
- Lymphoma (cancer of immune cells)
Vascular problems:
- Mesenteric problems of vascular insufficiency (blockages of arteries or veins)
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm (swelling of the main arteries in the abdomen)
Inflammatory diseases in the middle and lower abdomen:
- Enteritis (small intestine infection, Crohn's disease)
- Colitis (infection or inflammation of the colon)
- Diverticulitis (inflammation of the pouches that form in the colon)
- Appendicitis
Intestinal obstruction:
- Adhesions (scars on the abdomen that have lost their shape after surgery or have become inflamed)
- Tumor
- Inflammation
- Colon cancer
- Pain in the urinary tract:
- Kidney stones
- Urinary tract infections (kidneys, bladder)
- Tumors of the kidneys or bladder
Pelvic problems in women:
- Ovarian cysts
- Cancer
- Tubal infection (salpingitis)
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Myomas uterine tumors
- Malignant tumors of the uterus or cervix
- Endometriosis
- Adhesions (scars)
While there are several possible causes of bowel pain and abdominal pain, there are seven most common causes of bowel pain:
- Intestinal diseases
- Food poisoning
- Gases
- Upset stomach or heartburn
- Pain in the abdominal muscle
- Menstrual pain
- Constipation
These organs include:
- The organs associated with digestion are the stomach, tissues at the end of the esophagus, small and large intestines, liver, gallbladder and pancreas.
- The abdominal aorta is a large blood vessel that runs directly from the chest into the abdominal cavity.
- The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs that lie deep in the abdominal cavity.
However, there are cases when the pain may originate from another place, such as the chest or pelvic area. It may also be a generalized infection, such as flu or sore throat, that has affected the entire body. In addition, pain of intestinal origin can be localized anywhere, since the borders of the abdomen are quite large. The abdomen is an anatomical area that borders the lower edge of the ribs and above, the pelvic bones on each side. Therefore, the pain can radiate to these areas and be quite severe.
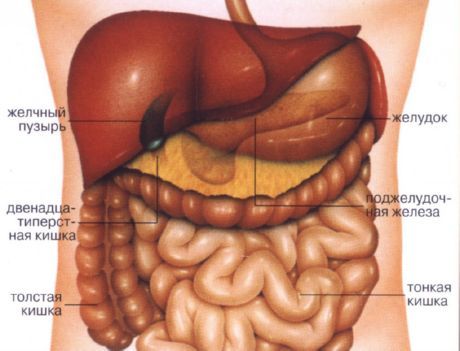
Referred pain in the intestines
In rare cases, intestinal pain that is felt in the abdomen is not related to the abdominal organs. There is a theory that explains this simply: abdominal pain has an unusual ability to travel along deep nerve pathways and exit in areas far from the source of the problem. For example, the lower part of the lungs, kidneys, uterus, and ovaries can project pain into the abdomen. This type of pain is called radiating, referred, or wandering pain because, although it is localized outside the abdominal cavity, it is precisely about the problem in the abdominal area.
Some examples of referred pain include:
- The right shoulder can project pain to the diaphragm, gallbladder, liver capsule...
- The left shoulder can project pain to the diaphragm, spleen, part of the pancreas, stomach, flexure of the spleen, lungs...
- Pain in the right shoulder blade can radiate to the gallbladder, bile ducts...
- Pain in the left shoulder blade can radiate to the spleen, part of the pancreas
Bowel pain can also be:
Visceral, associated with organs that are in spasm
Intestinal pain associated with the lower abdominal area - it is often sharp and persistent. Pain arising from inflammation in the abdomen is quite persistent. This pain is aggravated by tension in the peritoneum as a result of positional changes.
Pain associated with abdominal vascular disorders (thrombosis or embolism) may be sudden or gradual at onset, and severe or moderate at end. Pain associated with a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm may radiate to the back, side, or genitals.
The problem is that the intensity of pain does not always reflect the severity of the condition causing it. That is why any pain should be reported to a doctor as soon as possible. The severity of the condition has more to do with the suddenness of the pain, especially if it is a sharp pain localized to one region rather than spreading throughout the entire abdominal cavity.
Abdominal wall pain:
- Shingles (herpes zoster infection)
- Inflammation of the rib cartilage
- Trauma (causing muscle strain)
- Nerve irritation (neuropathy)
- Hernias
- Scars
- Inflammatory diseases of the upper abdomen:
- Peptic ulcer (duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer)
- Esophagitis (gastroesophageal reflux disease)
- Gastritis (irritation of the stomach lining)
- Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
- Cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder)
- Choledocholithiasis (passage of gallstones through the bile duct)
- Hepatitis (infection or inflammation of the liver)
- Colitis (infection or inflammation of the colon)
Localization of intestinal pain

Pain around the navel
Pain that is localized near the navel may be associated with a minor intestinal disorder or inflammation of the appendix. This condition is called appendicitis. The painful area is a small organ, a few fingers thick, that protrudes outward from the colon in the lower right part of the abdomen. If the passage of food through it is obstructed, inflammation may develop and the appendix will fill with pus.
Pain above the middle of the abdomen
The central area of the abdomen is called the epigastric region. Pain in this area is most often associated with stomach disorders. Persistent pain in this area may also indicate a problem with the duodenum, pancreas, or gallbladder.
Pain in the upper left abdomen
Although people very rarely experience pain in the place where it is actually present, it can be assumed that this is a problem with the colon, stomach, spleen and pancreas.
Pain in the upper right abdomen
Inflammation of the gallbladder often causes severe pain in the upper right abdomen.
Pain in the lower abdomen
Pain below the belly button may indicate that there are signs of a colon disorder. In women, pain in this area may also indicate a urinary tract infection or pelvic inflammatory disease.
Pain in the lower left abdomen
Pain in this part of the abdomen most often indicates a problem in the lower colon. There are several conditions that can affect this area, such as inflammatory bowel disease or an infection in the colon known as diverticulitis.
Pain in the lower right abdomen
Inflammation of the colon can cause pain in the lower right abdomen. Pain from appendicitis can also spread to the lower right abdomen.
How to understand the nature of intestinal pain?
Abdominal pain can be a manifestation of various diseases, including those of the intestines, and yet a person can rarely say that the pain comes from the intestines.
Although both intestinal pain and abdominal pain can be localized in the tissues of the abdominal wall that surround the abdominal cavity, the term "abdominal pain" is generally used to describe pain originating from the abdominal organs.
Types of pain in the intestines
Abdominal pain can be acute and sudden at the beginning or chronic and long-lasting at the end.
In terms of intensity, abdominal pain may be minor and not particularly worry a person, or it may reflect underlying problems associated with one of the abdominal organs.
When should a person worry about his condition?
The patient should know that intestinal pain is always an abnormal condition, but there is no need to panic. Although some types of pain may indicate a serious illness, emergency medical care is not always needed in this case. But moderate pain or chronic pain should still be discussed with a doctor. Severe pain should be diagnosed as soon as possible. Therefore, if you have severe intestinal pain, you should definitely go to the clinic.
Some of the serious symptoms of intestinal pain are
- elevated temperature
- diarrhea,
- persistent constipation,
- blood in stool,
- persistent nausea or vomiting,
- vomiting blood,
- severe pain in the abdominal area,
- jaundice
- swelling in the abdominal area
Treatment of intestinal pain
The drugs most commonly used for this purpose are:
Antidepressants, such as amitriptyline. These drugs can be taken in very low doses to minimize side effects.
Anti-inflammatory drugs: These drugs are sometimes used to reduce inflammation or affect the functioning of internal organs, thereby relieving pain.
Analgesics: Sometimes pain needs to be treated with drugs that reduce intestinal pain.
Tips to Reduce Bowel Pain
Intestinal diseases, food poisoning or abdominal muscle pain in children can be relieved by warming the tummy in a hot bath.
Pain in the intestines due to gases – here you should apply a tummy massage to try to dislodge the gas bubbles together. A warm bath can help with this difficult task.
Upset stomach or heartburn – medications such as antacids, which are usually used to relieve heartburn, can help here. Drinking warm milk can also soothe heartburn.
Pain in the intestines is a symptom that very seriously indicates some diseases. This pain can be reduced or cured, you just need to see a doctor in time.


 [
[