
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Neuroleptic syndrome
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025

Neuroleptic syndrome (NMS) is a rare but life-threatening condition, a unique reaction of the body to taking neuroleptic drugs, which is characterized by the appearance of elevated body temperature, muscle rigidity, changes in mental state, and disruption of the regulation of the autonomic nervous system. NMS most often develops shortly after the start of treatment with neuroleptics, or after an increase in the dosage of the drugs taken.
Epidemiology
Neuroleptic syndrome occurs with a frequency of 0.07-2.2% of cases in patients taking neuroleptics. It is more common in men than in women in a ratio of 2:1. The average patient age is 40 years.
If treatment of the underlying disease has already begun, the frequency of neuroleptic syndrome will depend on several factors - the selected drug, the patient's physical and mental state, and previous head injuries. The first signs develop at the beginning of treatment, on the 15th-21st day. A third of cases of NS are more likely associated with the peculiarities of the treatment regimen - a rapid increase in dosage or the introduction of additional groups of drugs with an enhanced effect. One example is when treating with aminazine and haloperidol, to achieve an antipsychotic effect more quickly. Also, extrapyramidal changes can worsen due to the abrupt withdrawal of drugs - "withdrawal syndrome".
Neuroleptic syndrome and malignant neuroleptic syndrome develop not only in patients with a healthy psyche, but also in those who have a history of schizophrenia, affective disorders, schizoaffective psychosis, as well as pathologies of the brain acquired in utero or during childbirth (toxicosis during pregnancy in the mother, prematurity, infections suffered by the mother in the first half of pregnancy, umbilical cord entanglement and strangulation, birth injuries, prematurity). These facts indicate that the patient's brain has already received organic damage at an early age and is more vulnerable.
As for those patients who do not have a history of early organic brain damage, intolerance to neuroleptic drugs can provoke a violation of water-electrolyte balance and exhaustion.
Causes neuroleptic syndrome
NS refers to a group of neurological disorders that develop as a result of taking antipsychotic drugs. By the nature of the manifestation of NS are very multiform, they can be both acute and chronic. At the dawn of the development of the treatment regimen with aminazine, brain changes were considered normal phenomena, and many doctors believed that this was a sign of positive dynamics of treatment. However, over time, a deeper study of this phenomenon revealed a number of very serious and, in some cases, irreversible psychosomatic changes.
However, the highest quality treatment results are achieved after using neuroleptics, even if we do not take into account the fact that a third of cases of Parkinson's disease are provoked by their use. NS has a negative impact on a person's personality - he becomes asocial, loses his ability to work, and his quality of life decreases.
There are three stages of manifestation of the disorder - early, protracted and chronic. According to the nature of the symptoms, there are the following forms:
- neuroleptic parkinsonism;
- acute dystonia;
- akitosia;
- tardive dyskinesia;
- neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
The reasons for the development of neuroleptic syndrome when taking antipsychotics have not yet been fully identified. Doctors have proposed a hypothesis that the cause of the disorder is that dopamine receptors are blocked, which leads to an imbalance of neurotransmitters and the cessation of communication between the thalamus and subcortical structures.
Risk factors
Neuroleptic syndrome can develop not only from taking antipsychotics, but also for other reasons. Risk factors for the development of neuroleptic syndrome:
Long-term therapy with atypical antipsychotic drugs:
- butyrophenones - haloperidol, domperidone, benperidol;
- phenothiazines – dibenzothiazine, thiodiphenylamine, paradibenzothiazine;
- thioxanthenes - clopixol, truxal, fluanxol.
Side effects of drugs in antipsychotic treatment:
- high initial doses of neuroleptics;
- treatment with high-component neuroleptics without a clear dosage;
- injection of neuroleptics;
- treatment of the underlying mental illness in case of overt extrapyramidal disorder;
- increasing the dosage of drugs too quickly;
- administration of drugs incompatible with neuroleptics.
Recording in the anamnesis of characteristic features:
- prescribing ECT without diagnosis and monitoring of well-being;
- the fact of dehydration;
- the fact of physical exhaustion (insufficient or inadequate nutrition);
- fact of psychomotor agitation;
- catatonia;
- chronic alcoholism;
- water-electrolyte imbalance;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland.
Organic damage to the brain tissue:
- traumatic brain injury;
- encephalopathy due to trauma;
- dementia;
- persistent extrapyramidal disorder.
Pathogenesis
The essence of the neurological disorder is weak neural conductivity near the basal nuclei. The pathogenesis of neuroleptic syndrome is in the suppression of dopaminergic neurotransmission, which causes extrapyramidal disorders and increased muscle tone. As a result, calcium is released and muscle tissue is gradually destroyed. At the same time, the vegetative centers in the hypothalamus are blocked, which leads to loss of control over heat production and is the cause of high temperature. Also, dopamine blockade of the vegetative nuclei leads to hypercatecholaminemia, hypersympathicotonia, and hypercortisolemia. These changes are abnormal and pose a direct threat to life.
However, treatment with neuroleptics may not always cause severe neurological changes. Predisposing factors also play an important role - the treatment regimen and duration, primary and additional drugs, craniocerebral injuries and the patient's physical condition.
Antipsychotics are very strong drugs, and when taken for a long time, self-medicated, or when the prescribed doses are increased, they can lead to serious psychosomatic changes, disability, and asocialization. Therefore, they should be taken with caution, and the patient should be given the necessary help and support.
Symptoms neuroleptic syndrome
Neuroleptic syndrome is based on a group of symptoms, which, if noticed at an early stage, can help avoid serious mental disorders in the future. Key symptoms of neuroleptic syndrome:
- worsening muscle weakness and high temperature. May be expressed as slight hypertonicity of muscles and may reach the point of inability to move (the "lead pipe" symptom).
- the appearance of symptoms from the group of extrapyramidal disorders - the appearance of chorea, dysarthria, bradykinesia, inability to swallow due to spasm of the masticatory muscles, uncontrolled eye movements, "wandering gaze", hyperexpressive facial expressions, increased reflexes, trembling of the hands, legs, head, inability to maintain balance, loss of space, difficulty walking.
- high temperature, up to 41-41 degrees, requiring urgent medical intervention.
- somatic deviations - the appearance of tachycardia, jumps in blood pressure, pale skin and hyperhidrosis, salivation, enuresis.
- water-electrolyte imbalance, exhaustion - sunken eyes, dry mucous membranes, flabby skin, coating on the tongue.
- mental disorders - anxiety, delirium, the appearance of catatonia, clouding of consciousness.
First signs
NS, as a rule, does not begin abruptly, therefore the first signs of neuroleptic syndrome will help to recognize the onset of the disease in time, when it can be stopped very quickly and without harm to health.
Bradykinesia - difficulty of movement becomes noticeable, they are slow, turns are difficult. Movements occur in an incomplete volume, stepwise - the "cogwheel" symptom, the patient cannot maintain balance, it becomes difficult to move, tremors spread to the head, arms, legs, facial expression is more like a mask, speech is slow or absent, salivation is increased. Mental changes in personality become more noticeable - depression, unsociability, bad mood, inhibition of thinking.
This syndrome develops in the first week of therapy and is more common in older people.
Parkinsonism is especially pronounced when treated with weakly binding neuroleptics (haloperidol, fluphenazine, triftazine). Parkinsonism is extremely rare when treated with atypical antipsychotics.
Drug-induced parkinsonism is short-lived and goes away after treatment is stopped, but there have been sporadic cases where the symptoms are irreversible and persist for life.
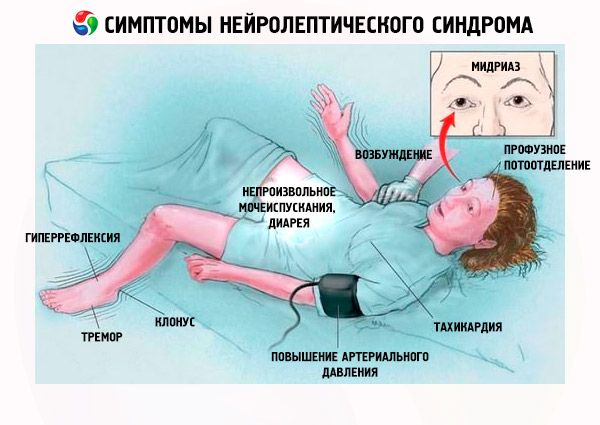
Thus, the first clinical signs of neuroleptic syndrome are as follows:
- Muscle rigidity.
- Hyperthermia (temperature > 38 ° C).
- Sweating.
- Salivation.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Dysphagia.
- Dyspnea.
- Tachypnea, respiratory distress (in 31% of cases).
- Tachycardia.
- Increased or labile blood pressure.
- Hypoxemia.
- Tremor.
- Incontinence of urine and feces.
- Gait disturbance.
- Psychomotor agitation.
- Delirium, lethargy, stupor, coma.
 [ 25 ]
[ 25 ]
Stages
The exact causes of extrapyramidal disorders have not been identified, but most specialists in the field of psychiatry and neurology adhere to the hypothesis of blockade of dopamine receptors with subsequent destruction of the connection between the thalamus and the subcortical zone. Disorders can be provoked by taking any neuroleptic drugs, but are most pronounced after therapy with typical antipsychotic drugs.
The following stages of neuroleptic syndrome are distinguished:
- Formation of neuroleptic parkinsonism. Movements become intermittent, the person is inactive, facial muscles are motionless, salivation and sweating appear, it is difficult to concentrate, the ability to remember and assimilate information decreases, interest in the surrounding world is lost.
- Acute dystonia. Occurs either at the beginning of drug therapy or after increasing the dosage of the main drug. Involuntary muscle spasms appear, causing discomfort, and in severe cases leading to joint dislocations.
- Early or late forms of akathisia. Increased motor skills, need for movement, actions. The person feels anxious, worried, constantly touches or tugs at clothes. The condition is often aggravated by depression, which complicates the course of the initial disease and can even lead to suicide.
- Condition of tardive dyskinesia. Develops after a long period from the beginning of treatment, occurs mainly in old age. Characterized by muscle spasms, gait distortion, problems with socialization, speech disorders.
- Formation of malignant neuroleptic syndrome. MNS accounts for a quarter of all cases of complications after treatment with neuroleptics. The danger is that even with emergency hospitalization and intensive therapy, a favorable outcome is not guaranteed and personality changes are already irreversible.
Forms
Depending on the rate of development, it is customary to distinguish acute, protracted and chronic neuroleptic disorder. In the acute form, developing in the early stages of treatment, no serious irreversible changes are observed. To normalize the condition, it is sufficient to cancel or reduce the dose of neuroleptics.
A protracted course is observed with long-term therapy with antipsychotic drugs, but this condition is more severe, and depending on the severity of the lesions, treatment under observation in a hospital setting may be required. Symptoms disappear within a few months after discontinuation of the drug.
The chronic form occurs against the background of a fairly long-term use of neuroleptics; all changes are already irreversible and are not corrected depending on the tactics of drug treatment.
Symptoms that unite types of neuroleptic syndrome:
- Lethargy, sluggishness, poor orientation in space, problems with movement, muscle spasms and tremors.
- Apathy, depressive mood, asociality.
- In case of malignant progression – complete immobility, lack of contact, hyperthermia.
NS is a very serious condition that requires not only competent and timely treatment, but also patient care to prevent the development of secondary infection, bedsores, pneumonia and accidental injury.
Malignant neuroleptic syndrome
As a result of prolonged neuroleptic therapy, such a life-threatening complication as malignant neuroleptic syndrome develops. However, it can also develop after taking other drugs that block dopamine receptors. MNS accounts for a quarter of all cases of complications after treatment with neuroleptics. The danger is that even with emergency hospitalization and a course of intensive therapy, a favorable outcome is not guaranteed and personality changes are already irreversible.
It is important to differentiate malignant neuroleptic syndrome from other diseases in order to provide assistance at an early stage. The clinical picture is most similar to:
- serotonin syndrome;
- lethal catatonia;
- infectious diseases - encephalitis, tetanus, meningitis, rabies, sepsis;
- epileptiform state;
- withdrawal (alcohol, barbiturate, sedative);
- ischemic stroke;
- malignant form of hyperthermia;
- heat stroke, overheating;
- poisoning with drugs (amphetamine, salicylates, heavy metal salts, organophosphorus compounds, anticholinergics, strychnine, lithium);
- autoimmune disorders;
- CNS tumors.
Extrapyramidal neuroleptic syndrome
Treatment with neuroleptics in the vast majority of cases leads to motor, autonomic and mental disorders. Extrapyramidal neuroleptic syndrome is a set of symptoms indicating damage to the pyramidal structures of the brain. This category includes cases of parkinsonism, dystonia, tremors of the hands, head, chorea, akathisia, myoclonic seizures. Motor disorders caused by taking antipsychotics are divided into:
- Parkinsonism. Characterized by a mild course, mirror-like lesions, high prolactin levels, slowness of movement, inhibition, loss of balance, wandering gaze, weakness, and limited range of motion.
- Acute dystonia.
- Acute akathisia. Characterized by anxiety, constant need to move, repetitive movements, depression, asociality.
- Tardive dyskinesia.
Extrapyramidal neuroleptic syndrome can be provoked by taking other medications (calcium antagonists, antidepressants, cholinomimetics, lithium preparations, anticonvulsants). Extrapyramidal disorders require specialized medical care in a hospital setting; without appropriate treatment, there is a high risk of death.
 [ 31 ], [ 32 ], [ 33 ], [ 34 ], [ 35 ], [ 36 ], [ 37 ], [ 38 ], [ 39 ]
[ 31 ], [ 32 ], [ 33 ], [ 34 ], [ 35 ], [ 36 ], [ 37 ], [ 38 ], [ 39 ]
Neuroleptic deficit syndrome
Treatment with typical neuroleptics leads to a neuroleptic defect, which is not always reversible after their withdrawal. Neuroleptic deficit syndrome is characterized by affective disorder, suppression of cognitive and social functions. The symptoms are largely similar to the development of schizophrenia and are divided into primary and secondary. Primary is directly related to the disease, while secondary is related to the side neuroleptic effect and can be corrected with medication.
Neuroleptic deficit syndrome has the following symptoms:
- Depression of willpower, sluggish, uninitiative state, lack of emotional reaction to events. Interest in life decreases, motivation is absent, usual interests do not cause any reaction, the person limits the circle of communication and withdraws into himself.
- Slowing down of motor and mental activity, decreased speed of thought, inability to concentrate on a task, decreased memory, a feeling of “emptiness” in the head, and, as a consequence, decreased intelligence.
- Withdrawal from society, detachment, depressive state, accompanied by sleep disturbance, anxiety, irritability and anger, akathisia. In practice, there are cases when neuroleptic syndrome without proper treatment and care, combined with depression, led a person to suicide.
Acute neuroleptic syndrome
Depending on the duration of the disease, it is customary to distinguish between acute, protracted and chronic variants of the course of neuroleptic syndrome. Acute neuroleptic syndrome is an early form of the disease, developing in the first days of drug treatment of the underlying disease. At this stage, abrupt withdrawal of the drug leads to the initial state.
The course of the disease is accompanied by a number of symptoms that cannot be grouped as unique, which significantly slows down differential diagnostics. Common signs include slowness of movement, clouding of consciousness, impaired thinking, difficulty in moving ("cogwheel"), impaired coordination, trembling of hands and head (Parkinsonism). The patient is uncommunicative, does not show emotions, is withdrawn, facial expressions are inexpressive. A characteristic feature is hyperkinesis (obsessive, cyclically repetitive movements that cannot be stopped by willpower, only after the administration of sedatives).
If you continue taking the medications, it may transform into the most severe form - malignant neuroleptic syndrome. In addition to the above-mentioned neuropsychiatric symptoms, somatic changes also appear - high temperature (41-42 degrees), complete immobility. If intensive therapy is not administered at this stage, then the probability of death is high.
Complications and consequences
Any drug, in addition to a positive effect, has another effect on the body. This is especially true for neuroleptic drugs. If they are taken for a long period of time or the dosage is increased sharply, the following consequences and complications of neuroleptic syndrome develop:
- All movements are accelerated, a person needs to move all the time, walk, and very quickly. It is possible to suspend a person's motor activity only with the help of sedatives.
- Another characteristic feature is constant eye movement - the gaze is fleeting, does not fixate on anything for a long time, there is a pronounced mimic play, the person often sticks out his tongue. Along with this, the appearance of hyperlordosis is noted.
- The facial muscles are affected, which leads to a change in the usual facial features, this condition may remain fixed.
- Along with physical changes, treatment with neuroleptics is accompanied by depressive states.
- Gastrointestinal disorders - slow salivation, heaviness in the epigastrium, a feeling of "bursting" in the liver area.
With abrupt withdrawal of neuroleptics, aggression, pain in the whole body, aches, sleep disturbances, depressive states appear - the patient is tearful, restless. The most dangerous thing with abrupt withdrawal of the drug is that a relapse of the underlying disease, which was fought with the help of these drugs, may occur. In this situation, you need to contact your doctor with the problem so that he can reduce the optimal dose of the drug. This will prepare the body for the completion of the course and will not cause much harm at the psychosomatic level.
Other potential complications of neuroleptic syndrome include:
- Acute skeletal muscle necrosis.
- Renal failure.
- Cardiac arrhythmias and myocardial infarction.
- Aspiration pneumonia.
- Respiratory failure.
- Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis.
- Liver failure.
- DIC syndrome.
- Relapse of psychiatric illness after discontinuation of neuroleptics.
Diagnostics neuroleptic syndrome
Extrapyramidal syndrome as such does not have generally accepted diagnostic criteria, therefore, the diagnosis of neuroleptic syndrome is reduced to the exclusion of similar pathological conditions. However, differentiation may be difficult in lethal catatonia, malignant hyperthermia of non-hereditary nature, serotonin syndrome. For confirmation, anamnesis is collected, a series of analyses and functional tests are carried out, and all necessary studies are prescribed.
 [ 48 ], [ 49 ], [ 50 ], [ 51 ], [ 52 ]
[ 48 ], [ 49 ], [ 50 ], [ 51 ], [ 52 ]
Tests
The most informative tests for neuroleptic syndrome are based on the study of biologically active fluids of the body, namely:
- conducting a general blood test (increased ESR to 70 mm/h, low percentage of leukocytes, low percentage of protein fractions in the serum sample, urea and creatinine above normal).
- urine for clinical analysis;
- arterial blood to determine the level of gas content in it. (increased nitrogen content).
- liver function tests;
- blood serum and urine for toxicological testing;
- puncture for analysis of cerebrospinal fluid to exclude meningitis, encephalitis, etc.;
- determination of blood clotting rate.
If the tests show significant deviations from the norm, instrumental and differential diagnostics exclude other diseases, the patient with neuroleptic syndrome requires hospitalization and further treatment. Depending on the form and stage of the disease, we can talk about the further prognosis for the patient's health.
 [ 53 ], [ 54 ], [ 55 ], [ 56 ], [ 57 ], [ 58 ], [ 59 ]
[ 53 ], [ 54 ], [ 55 ], [ 56 ], [ 57 ], [ 58 ], [ 59 ]
Instrumental diagnostics
The most informative laboratory tests include the study of biologically active fluids of the body, namely:
- conducting a general blood test;
- urine for clinical analysis;
- arterial blood to determine the level of gas content in it;
- liver function tests;
- blood serum and urine for toxicological screening;
- puncture for analysis of cerebrospinal fluid;
- determination of blood clotting rate.
Instrumental diagnostics of neuroleptic syndrome takes place in two stages:
- organization of chest radiography;
- the purpose of electroencephalography is to monitor the electrical conductivity of impulses in the brain.
The results of the NS tests indicate the following data:
- detection of leukocytosis, shift of the formula to the left;
- high creatine phosphokinase;
- confirmation of metabolic acidosis.
Malignant neuroleptic syndrome is indicated by electrolyte imbalance, high alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, aldolase, lactate dehydrogenase or lactic acid, low serum iron, high blood nitrogen, muscle protein breakdown and its appearance in the urine.
Differential diagnosis
It can be quite difficult to recognize neuroleptic syndrome at an early stage, mainly because its symptoms are attributed to the underlying disease. It is also dangerous to miss the first symptoms because late differential diagnosis of neuroleptic syndrome leads to its malignancy, which worsens the patient's psychosomatic condition and may be irreversible.
Diagnosis and differentiation of this condition is difficult due to the wide range of similar conditions. During examination, it is necessary to exclude the fact:
- benign neuroleptic extrapyramidal syndrome (occurs without an increase in temperature);
- loss of clarity of consciousness, rhabdomyolysis processes);
- catatonic state (it is necessary to clarify the data when collecting anamnesis);
- meningitis;
- encephalitis;
- hemorrhages in the subcortex of the brain (confirmed after a lumbar puncture);
- heat stroke (the skin is dry and the muscles, in comparison with the nervous system, are hypotonic);
- exclude the possibility of malignant hyperthermia (the history may include pain relief using a halogenated anesthetic, succinylcholine injections);
- non-convulsive epilepsy;
- fevers of infectious etiology;
- serotonin syndrome (history of taking antidepressants, diarrhea, nausea, but no significant muscle wasting);
- poisoning (amphetamines, cocaine, alcohol, barbiturates).
Who to contact?
Treatment neuroleptic syndrome
Medical tactics in the event of neuroleptic syndrome in patients require the fastest possible discontinuation of the main neuroleptic drug with subsequent step-by-step restoration of all functions. Treatment of neuroleptic syndrome is carried out as follows:
- The administration of neuroleptics or other drugs that caused the disturbances (lithium, antidepressants, setrons) is stopped.
- Discontinuation of administration of drugs that aggravate the manifestations of rhabdomyolysis.
- Removal of drug residues, detoxification – gastric lavage, intestinal lavage, administration of enterosorbent, administration of diuretics and, if indicated, plasma purification.
- Dantrolene is prescribed - a drug that blocks the release of calcium from muscle cells, eliminates muscle tension, normalizes temperature and blocks the growth of rhabdomyolysis.
- Conducting an electroconvulsive therapy procedure.
- Introduction of dopamine antagonists and drugs that correct it - amantadine, bromocriptine. It is necessary to prescribe cyclodol, mydocalm, baclofen. To reduce muscle tone.
- To release dopamine – dexamethasone, methylprednisolone.
- Restoration of water and electrolyte balance. Monitoring of electrolyte levels, sugar, preventive measures regarding kidney function.
- Prevention of the development of gastric ulcer – administration of ranitidine, omeprazole.
- Prevention of blood clots.
- Normalization of body temperature, antiperitoneals, lytic mixture, cold on large arteries.
- Continuous patient care – prevention of bedsores and pneumonia.
Delirious state after taking cyclodol, bomocriptine pose minimal danger and are easily blocked with sedatives, but hyperthermia, muscle spasms and immobility pose a direct threat to life.
Emergency care for neuroleptic syndrome
Neuroleptic syndrome can be called a negative consequence of treatment with antipsychotic drugs. Emergency care for neuroleptic syndrome is aimed at eliminating life-threatening symptoms. Symptoms manifest themselves in three areas:
- Vegetative. The appearance of tachycardia, decreased blood pressure, sweating, salivation, urinary incontinence, pale skin, photosensitivity, lethargy and general weakness.
- Neurological. Increased tone of smooth muscles, decreased flexibility of the limbs like a "cogwheel", convulsions, trembling of the arms, legs, head, hypermobility. The muscles of the facial skull and facial expressions are immobile ("mask-like"), the appearance of Kulenkampff-Taranov syndrome (convulsions of the swallowing muscles combined with the need to stick out the tongue).
- Mental. The appearance of anxiety, internal restlessness, hypermobility, importunity, sleep problems.
The most dangerous condition during treatment with neuroleptics is malignant neuroleptic syndrome. It is characterized by critical hyperthermia, vegetative disorders, and the development of toxic dermatitis.
Emergency care for neuroleptic syndrome consists of the following:
- Complete discontinuation of neuroleptics and hospitalization in the intensive care unit.
- Administration of antipyretic drugs.
- Combating dehydration and water-electrolyte imbalance.
- Amantadine intravenously, after stabilization of the condition - orally.
- Benzodiazepines intravenously.
- Improving blood microcirculation.
- In case of breathing problems – artificial ventilation.
- Probing of the stomach through the nasal cavity – for nutrition and hydration.
- Heparin to improve blood fluidity.
- Preventive measures to prevent secondary infection.
- If necessary, electroconvulsive therapy may be performed.
 [ 60 ], [ 61 ], [ 62 ], [ 63 ]
[ 60 ], [ 61 ], [ 62 ], [ 63 ]
Drug treatment
Extrapyramidal disorders, like other psychosomatic disorders, require urgent drug correction. Drugs for neuroleptic syndrome are prescribed depending on the form and stage, so the dosage of basic drugs can be adjusted by the doctor.
In case of dyskinesia, to alleviate the condition, akinetone is prescribed in a dosage of 5 mg, if it is not available - aminazine, 25-50 mg by injection + 2% caffeine solution under the skin. Akineton cannot be prescribed with levodopa - this aggravates the dyskinetic disorder, when taken with alcohol, the work of the central nervous system is suppressed. Aminazine cannot be prescribed for cirrhosis, hepatitis, myxedema, renal failure, heart defects, thromboembolism, rheumatism, arthritis, as well as for alcohol, barbiturate, drug intoxication.
In case of extrapyramidal syndrome at the acute stage, antiparkinsonian correctors are administered - cyclodol from 6 to 12 mg, akinetone, injection of treblex (administer only in combination with fluspirilene in one injection) to relieve muscle spasms and normalize motor activity. Cyclodol should be prescribed under constant supervision of a doctor, since in high dosages it can provoke delirious states and vomiting.
Along with drug treatment, positive dynamics are achieved by conducting plasma purification, which completely eliminates extrapyramidal disorder in 2-3 procedures, weakens the manifestation of akinesia, muscle hypertonicity, tremor, hyperkinesia. Depressive state, melancholy pass, emotional state is normalized.
Prevention
The use of neuroleptic drugs should be under the supervision of the attending physician, with strict adherence to doses and periods of administration. Prevention of neuroleptic syndrome consists of monitoring the patient's physical and mental state and monitoring his vital functions.
If the mental disorder for which neuroleptics were prescribed requires continuation of therapy after the fact of neuroleptic syndrome in any form, then the repeated course can be resumed only after the symptoms of NMS have been eliminated.
In addition, a repeated course of neuroleptic drugs is carried out only under clinical supervision in a hospital setting. This is vitally important, as it will help prevent a relapse of neuroleptic syndrome and avoid life-threatening complications.
Neuroleptics are a very strong group of drugs; uncontrolled use and self-medication can lead not only to the suppression of brain function, loss of clarity of consciousness and social isolation, but also to death.
Forecast
Long-term use of neuroleptics often causes complications in the future. The prognosis of neuroleptic syndrome is further complicated by the fact that in most cases a secondary form of the disease develops, which is characterized by a severe course and a predominance of neurological disorders. This leads to a malignant course of the disease and can lead to death.
Among the pathologies developing on the basis of secondary and malignant neuroleptic syndrome, cases of rhabdomyolysis (muscle fiber depletion and tissue atrophy) and functional respiratory disorders have been recorded - cases of pulmonary embolism, aspiration pneumonia, pulmonary edema, respiratory distress syndrome. The digestive system is also affected (development of liver failure), the cardiovascular system (impaired rhythm, electrical conductivity of the heart up to its arrest), multifocal infections of the body (blood poisoning, infectious diseases of the genitourinary system), damage to the nervous system - development of cerebral insufficiency.
Without proper treatment, the primary fact of NS develops into a more severe form of the course, but even with proper treatment, relapses are not excluded. Therefore, the disease requires strict adherence to medical prescriptions and additional care for the person.
Currently, the mortality rate from neuroleptic syndrome is estimated at 5-11.6%. Mortality is caused by one or more complications (e.g., respiratory failure, cardiovascular collapse, renal failure, arrhythmia, thromboembolism, disseminated intravascular coagulation). Renal failure is the cause of death in 50% of cases.
 [ 70 ]
[ 70 ]

