
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Insulin in diabetes mellitus: when to prescribe, dose calculation, how to inject?
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
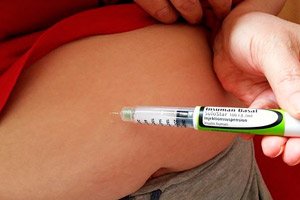
The hormone insulin produced by the pancreas is necessary to maintain glucose homeostasis, regulate carbohydrate and protein metabolism, and energy metabolism. When this hormone is insufficient, chronic hyperglycemia develops, most often indicating diabetes mellitus, and then insulin is prescribed for diabetes.
Insulin treatment for diabetes
Why do they inject insulin for diabetes? The task that insulin treatment for diabetes solves is to provide the body with this hormone, since in type 1 diabetes, the β-cells of the pancreas do not perform their secretory function and do not synthesize insulin. Endocrinologists call regular insulin injections for this type of diabetes insulin replacement therapy, aimed at combating hyperglycemia - an increased concentration of glucose in the blood.
And the main indications for the use of insulin preparations are insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Is it possible to refuse insulin in diabetes? No, insulin injections are necessary in type 1 diabetes, since in the absence of the endogenous hormone, this is the only way to regulate blood glucose concentration and avoid the negative consequences of its increase. At the same time, the pharmacological action of insulin, that is, insulin preparations, exactly reproduces the physiological effect of insulin produced by the pancreas. It is for this reason that insulin addiction does not develop in diabetes.
When is insulin prescribed for diabetes mellitus not associated with insulin dependence? Insulin in type 2 diabetes – with an increased need for insulin due to the resistance of receptors in some tissues to the hormone circulating in the blood and impaired carbohydrate metabolism – is used when the β-cells of the pancreas are unable to meet this need. In addition, progressive β-cell dysfunction in many obese patients leads to long-term hyperglycemia, despite taking drugs to lower blood sugar levels. And then the transition to insulin in type 2 diabetes can restore glycemic control and reduce the risk of complications associated with progressive diabetes (including diabetic coma).
Research published in 2013 in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology demonstrated the effectiveness of intensive short-term insulin therapy in 59-65% of patients with type 2 diabetes.
Also, insulin injections for this type of diabetes may be prescribed for a limited period of time in connection with surgery, severe infectious pathologies or acute and emergency conditions (primarily stroke and heart attack).
Insulin is used for gestational diabetes (the so-called gestational diabetes mellitus) - if it is not possible to normalize carbohydrate metabolism and curb hyperglycemia with the help of diet. But during pregnancy, not all insulin preparations can be used (only human insulin): an endocrinologist should correctly select the right drug - taking into account contraindications of the drugs and the blood sugar level of a particular patient.
Release form
Insulin preparations are available in the form of a solution and suspension for injection. These are either regular glass vials (hermetically sealed) for administration of the solution with an insulin syringe, or cartridge vials (penfills) for administration with special syringe pens.
Names of drugs of the insulin group: the best insulins for diabetes
Today, all insulin group drugs produced are classified depending on the speed with which they begin to act after administration and the duration of this action.
Names of fast-acting drugs similar to human insulin: Insulin aspart, Humalog, NovoRapid Penfill (NovoRapid FlexPen), Apidra (in other versions - Epidra). These drugs have an ultra-short effect at the very beginning (already 10 minutes after administration); the maximum (peak) effect is noted no later than 1.5-2 hours, and the sugar-lowering effect after a single administration lasts for about three to five hours.
Short-acting insulin preparations, which include Insulin C, Actrapid, Apidra SoloStar, Iletin, Insuman Rapid, Insulrap, Monosuinsulin MK, Gensulin R, Homorap, Humalog, Humodar R, etc., have an antiglycemic effect lasting 7-8 hours, and they begin to act 20-30 minutes after insulin injection in both types of diabetes.
Such drugs as Actraphan NM, Inuzofan (Isophaninsulin NM, Protofan NM), Insuman Basal, Insular Stabil, Lente, Iletin II Lente, Monotard, Homolong 40, Humulin NPH are insulins with an average duration of action (within 14-16 hours), while they begin to act only one and a half to two hours after injection.
It is believed that the best insulins for diabetes are those that can be injected once a day. Such a long-term effect of insulin in diabetes (almost 24-28 hours) and its stable concentration are provided by Lantus (Lantus OptiSet, Lantus SoloStar), Humulin Ultralente, Insulin Superlente, Tujeo SoloStar, Ultratard NM, Levemir Penfill (Levemir FlexPen).
Pharmacodynamics
After injection, insulin preparations enter the systemic bloodstream. Their pharmacologically active substances bind to globular plasma proteins (usually by more than 25%), and are then quickly removed from the blood and interact with insulin receptors on cell membranes - to improve intracellular glucose metabolism, helping to reduce its level in the blood.
Exogenous insulin is broken down by hydrolysis under the action of liver and kidney enzymes; elimination occurs with urine and bile.
The pharmacokinetics of long-acting insulin preparations are somewhat different, since their substance is released much more slowly. In addition, some synthetic insulins break down into active metabolites, which contribute to a prolonged hypoglycemic effect.
Dosing and administration
For absolutely all patients, insulin selection for diabetes of both types is carried out by the attending endocrinologist on an individual basis: based on the results of blood tests for fasting and 24-hour glucose levels, glycosylated hemoglobin, and urine tests for sugar (glucosuria); taking into account age, lifestyle, diet and nutritional status, as well as the intensity of normal physical activity.
Calculation of insulin for diabetes is carried out on the same principles with correlation of the type of diabetes. And the optimal dose of insulin for diabetes is established on the basis of determining the production of endogenous insulin and the daily requirement for this hormone - on average 0.7-0.8 U per kilogram of body weight for type 1 diabetes, and for type 2 diabetes - 0.3-0.5 U/kg.
In cases where the blood sugar level exceeds 9 mmol/l, a dose adjustment is necessary. It should be borne in mind that when 1 U of medium-acting insulin or prolonged insulin is administered, the blood glucose level decreases by approximately 2 mmol/l, and fast-acting drugs (ultra-short-acting) are significantly stronger, which must be taken into account when dosing them.
How, where and how many times to inject insulin for diabetes?
Insulin preparations are administered subcutaneously; insulin injections for diabetes are usually given in the subcutaneous tissue on the abdomen (on the anterior abdominal wall), on the front surface of the thigh, upper part of the buttocks or in the shoulder (below the shoulder joint - in the area above the deltoid muscle). The preparation should not be cold (this significantly slows down the onset of its action).
When using medium-acting insulins, a standard regimen is used, in which injections are given twice a day: in the morning, no later than 9 a.m. (30-40 minutes before meals), 70-75% of the total daily dose should be administered, and the rest no later than 5 p.m. (also before meals). Nutrition is very important for diabetes on insulin: 5-6 meals a day should be clearly distributed over time.
A single insulin injection for type 2 diabetes may be appropriate if the patient's daily insulin requirement does not exceed 35 U and there are no sharp fluctuations in glycemia levels. For such cases, long-acting insulin preparations are used, which require eating every four hours, including two hours before bedtime.
Since it is believed that the use of insulin once a day in patients with type 1 diabetes does not reflect the physiology of the action of this hormone, a scheme for its administration called intensive insulin therapy has been developed.
According to this scheme, both short-acting and long-acting insulin preparations can be used in combination. If the former (administered before meals) should cover the need for insulin after meals, the latter (used in the morning and before bedtime) provide other biochemical functions of insulin in the body. In general, this leads to the need to inject different preparations up to four to six times a day.
 [ 14 ], [ 15 ], [ 16 ], [ 17 ], [ 18 ], [ 19 ], [ 20 ], [ 21 ]
[ 14 ], [ 15 ], [ 16 ], [ 17 ], [ 18 ], [ 19 ], [ 20 ], [ 21 ]
Contraindications
Contraindications to the use of insulin include the presence of a hormonally active tumor of the islet β-cells of the pancreas (insulinoma), acute pancreatitis, acute viral hepatitis, severe liver and/or kidney failure, as well as ulcerative pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract during their exacerbation.
Why is insulin dangerous for diabetes?
In addition to such side effects as the appearance of a local allergic reaction (hyperemia and itching of the skin), swelling, muscle pain and atrophy of the subcutaneous tissue at the injection site, with an unbalanced dosage, the harm of insulin in diabetes can manifest itself in the form of hypoglycemia.
This is a decrease in glucose levels below the physiologically adequate level, which is manifested by the following symptoms: pale skin, cold sweat, decreased blood pressure and increased heart rate; headache and deterioration of vision; increased fatigue or general weakness and drowsiness; nausea and temporary changes in taste; tremors and convulsions; nervousness and anxiety; decreased concentration and loss of orientation.
In severe hypoglycemia, the brain stops receiving glucose, and a state of coma sets in, threatening not only irreversible degenerative changes in brain cells, but also death.
Overdose
Insulin overdose causes hypoglycemia (see above). Also, prolonged excess of insulin doses in patients with type 1 diabetes can lead to the development of Somogyi syndrome, which is also called rebound hyperglycemia.
The essence of chronic insulin overdose is that in response to a decrease in blood glucose levels, so-called counter-insulin hormones (adrenaline, corticotropin, cortisol, somatotropin, glucagon, etc.) are activated.
As a result, the content of ketone bodies in the urine can increase significantly (ketonuria is manifested by the acetone smell of urine) and ketoacidosis can develop - with a significant increase in diuresis, excruciating thirst, rapid weight loss, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, general lethargy, loss of consciousness, and even a comatose state.
Interactions with other drugs
In diabetes, insulin potentiates the action of hypoglycemic drugs for internal use; sulfonamides; tetracycline antibiotics; antidepressants of the MAO inhibitor group; calcium and lithium preparations.
Antiviral drugs, GCS, thiazide diuretics, heparin and ephedrine preparations, antihistamines should not be used with insulin injections. Interaction with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and preparations containing salicylic acid and its derivatives enhance the effect of insulin.
What is better: insulin or pills for diabetes?
Tablets related to hypoglycemic agents for oral administration have different mechanisms of action, and are used only for insulin-independent or insulin-resistant diabetes type 2. So it is the type of this disease that gives the endocrinologist the basis for prescribing insulin or tablets for diabetes.
Sulfonylurea derivatives – Glibenclamide (Maninil), Gipizide (Minidiab), Glicvidone, Gliclazide, as well as drugs of the glinide group (Repaglinide, Repodiab, Diaglinide, Novonorm) have a stimulating effect on the β-cells of the pancreas, increasing insulin secretion.
And drugs of the biguanide group, the active substance of which is butylbiguanide hydrochloride - Butylbiguanide, Buformin hydrochloride, Gliformin, Glibutide, Metformin hydrochloride, Dianormet, etc. - reduce the level of glucose in the blood of patients with type 2 diabetes by improving the transfer of glucose through the cell membranes of myocytes and fat cells. This affects the metabolism of glucose, and it, firstly, is not produced in another way (from non-carbohydrate compounds), and, secondly, does not enter the blood as a result of blocked breakdown of glycogen reserves in tissues. In some cases, these drugs are used simultaneously with insulin.
See also the publication - Tablets for diabetes
How to lose weight with diabetes on insulin?
Many people know that treating diabetes with insulin can add extra pounds in the form of subcutaneous fat tissue, since this hormone promotes lipogenesis.
The above-mentioned hypoglycemic drugs in tablet form, containing butylbiguanide as the active substance, help to reduce not only glycemia, but also appetite. When taken (one tablet per day), diabetics with obesity lose weight.
In addition, appropriate nutrition is necessary for diabetes on insulin with a restriction of daily calorie intake (within 1700-2800 kcal).
If diabetes is insulin-dependent, it is recommended to follow a diet for type 1 diabetes, and for patients with insulin-independent diabetes, a diet for type 2 diabetes has been developed.
Attention!
To simplify the perception of information, this instruction for use of the drug "Insulin in diabetes mellitus: when to prescribe, dose calculation, how to inject?" translated and presented in a special form on the basis of the official instructions for medical use of the drug. Before use read the annotation that came directly to medicines.
Description provided for informational purposes and is not a guide to self-healing. The need for this drug, the purpose of the treatment regimen, methods and dose of the drug is determined solely by the attending physician. Self-medication is dangerous for your health.

