
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
A giant cell tumor
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
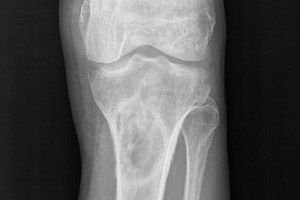
Diagnostics osteoclastomas
Radiographs and CT scans reveal a focus of destruction that affects the metaepiphysis of the tubular bone, with signs of destruction of the cortical layer and articular surface, often with prolapse of pathological masses into the joint cavity.
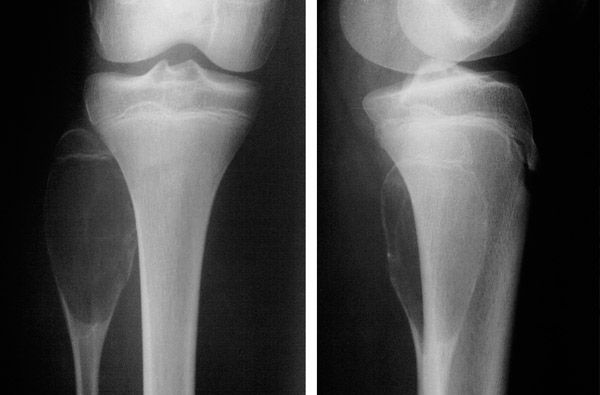
During scintigraphy, both local hypervascularization (on average 130%) and hyperfixation of the radiopharmaceutical (on average 325%) are noted.
What do need to examine?
How to examine?
Differential diagnosis
The tumor is differentiated from aneurysmal bone cyst and chondroblastoma.
Who to contact?
Treatment osteoclastomas
Treatment of giant cell tumor is surgical - radical resection of the tumor in combination with various options of bone auto- and alloplasty and the use of external fixation devices.


 [
[