
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Oral cavity (cavitas oris)
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 07.07.2025
The oral cavity (cavitas oris) is located in the lower part of the face and is the beginning of the digestive system. The oral cavity is limited below by the mylohyoid muscles, which form the muscular basis of the lower wall of the oral cavity - the diaphragm of the mouth (diaphragma oris). The upper wall of the oral cavity is formed by the hard and soft cerebellum, on the sides - by the cheeks, and in front - by the lips. At the back, the oral cavity communicates with the pharynx through a wide opening - the pharynx (fauces). The oral cavity is subdivided into a smaller anterior section - the vestibule of the mouth and the oral cavity proper. The vestibule of the mouth (vestibulum oris) is limited in front by the lips, on the sides - by the inner surface of the cheeks, behind and on the medial side - by the teeth and gums. The oral cavity proper (cavitas oris propria) is located between the gums and teeth.
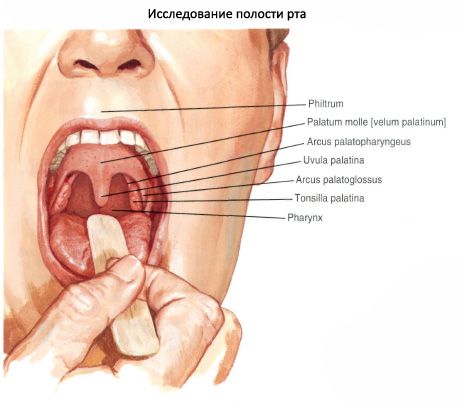
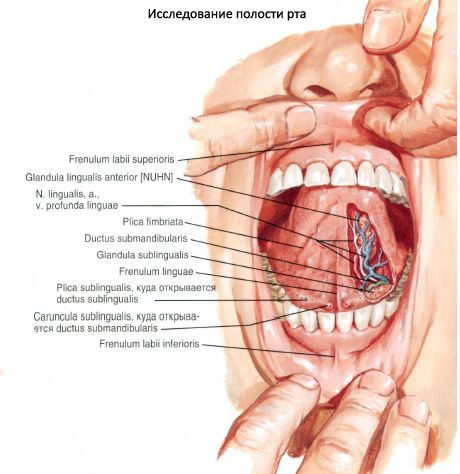
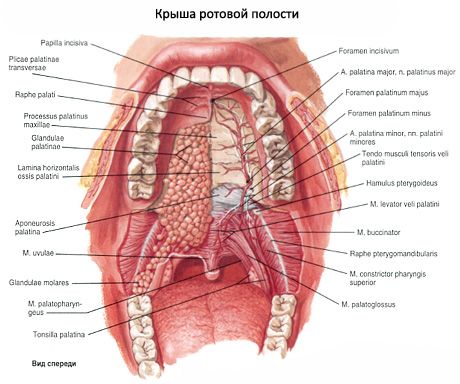
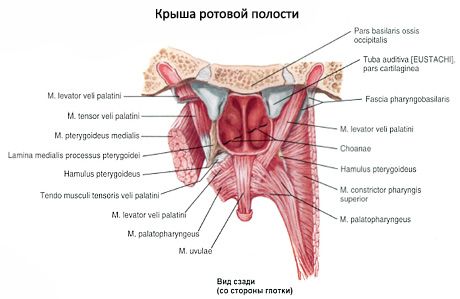
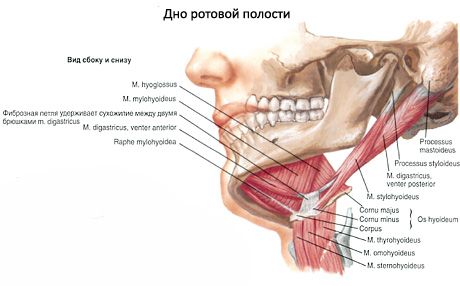
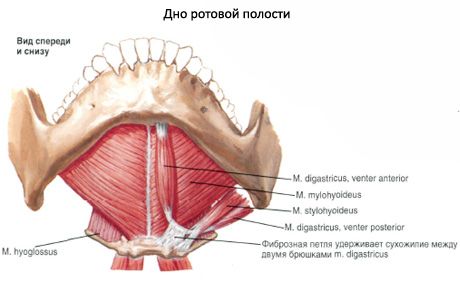
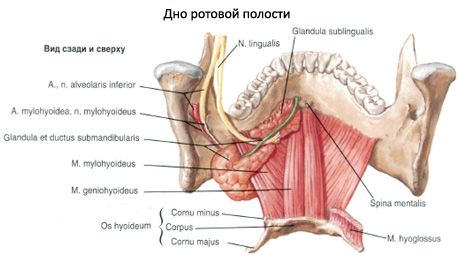
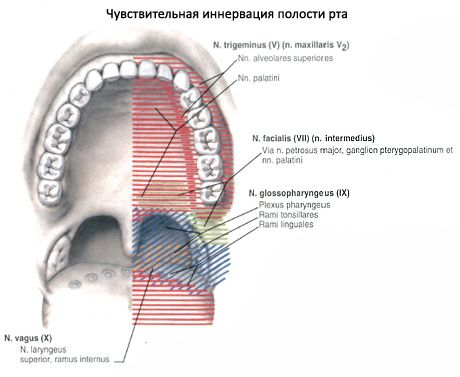
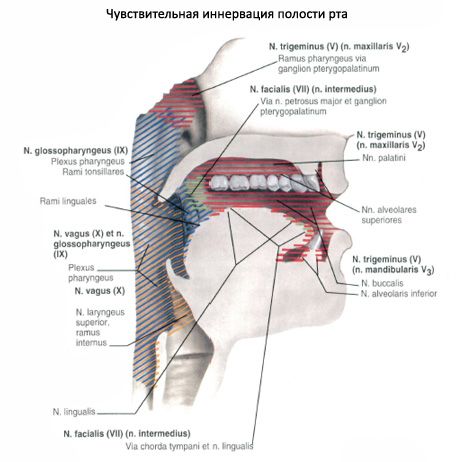
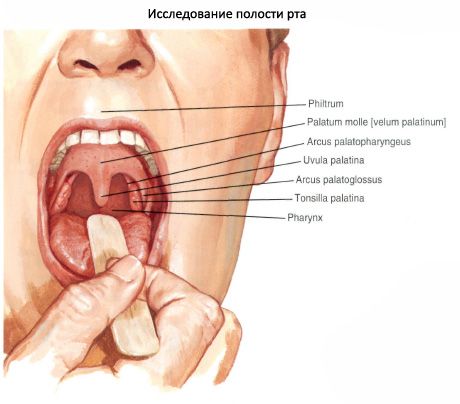
The gums are the alveolar processes of the upper jaws and the alveolar part of the lower jaw, covered with a mucous membrane. The vestibule and the oral cavity itself communicate through a narrow gap between the upper and lower teeth.
The oral slit (rima oris) is bounded by the upper and lower lips (labium superius et labium inferius), which are connected laterally on each side by the labial commissure (labial commissure). The basis of the lips is the orbicularis oris muscle. The mucous membrane of the lips in the vestibule of the mouth passes onto the alveolar processes and the alveolar part of the jaw, forming the frenulum of the upper lip and the frenulum of the lower lip (frenulum labii superioris et frenulum labii inferioris).
The cheeks (buccae) have the buccal muscle at their base. Between the muscle and the skin there is a cluster of fatty tissue - the fatty body of the cheek (buccae adiposum buccae), or the fat lump of Bish, most developed in infants. At this age, the fat lump thickens the wall of the oral cavity, helps reduce the effect of atmospheric pressure on the oral cavity and thus clouds sucking.
What do need to examine?

