
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Clavicular-shoulder muscle
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
The coracobrachialis muscle (m.coracobrachialis) begins at the apex of the coracoid process of the scapula, passes into a flat tendon that attaches to the humerus below the crest of the lesser tubercle at the level of attachment of the deltoid tendon. Some of the muscle bundles are woven into the medial intermuscular septum of the shoulder.
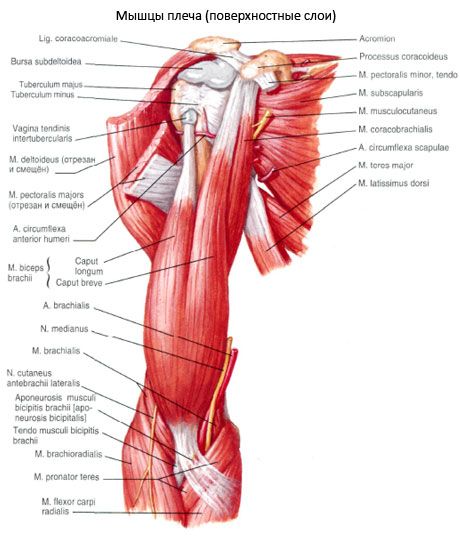
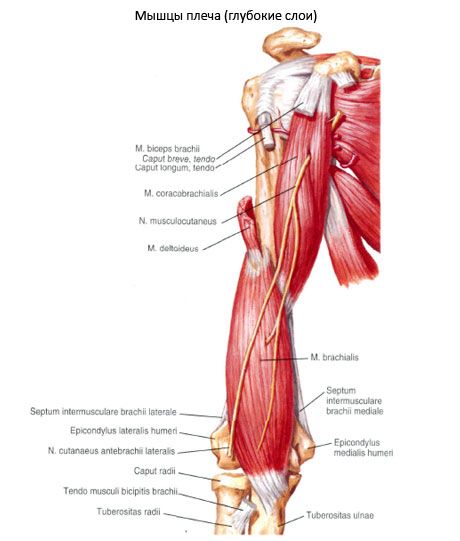
Function of the coracobrachialis muscle: flexes the shoulder at the shoulder joint and brings it toward the body. Participates in the external rotation of the shoulder (if the shoulder is pronated). If the shoulder is fixed, the muscle pulls the scapula forward and downward.
Innervation of the coracobrachialis muscle: musculocutaneous nerve (CV-CVIII).
Blood supply of the coracobrachialis muscle: anterior and posterior arteries surrounding the humerus.
Where does it hurt?
How to examine?


 [
[