
All iLive content is medically reviewed or fact checked to ensure as much factual accuracy as possible.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable media sites, academic research institutions and, whenever possible, medically peer reviewed studies. Note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to these studies.
If you feel that any of our content is inaccurate, out-of-date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Anoscopy
Medical expert of the article
Last reviewed: 04.07.2025
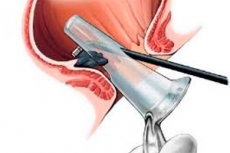
Indications
Anoscopy is of great importance for detecting hemorrhoids, differentiating true polyps from hypertrophied anal papillae, which are hyperplasia of the mucous membrane in the anal sinuses (Morgagni crypts) as a result of chronic inflammation in anal fissures, hemorrhoids or proctitis. Anoscopy helps to differentiate anal polyps from thrombosed internal hemorrhoids, which look like a rounded formation of a purple-bluish or whitish color, without the neck and stalk characteristic of polyps.
Anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy are used to evaluate symptoms and conditions of the rectum and anus (eg, obvious rectal bleeding, discharge, prolapse, rectal pain ).
Who to contact?
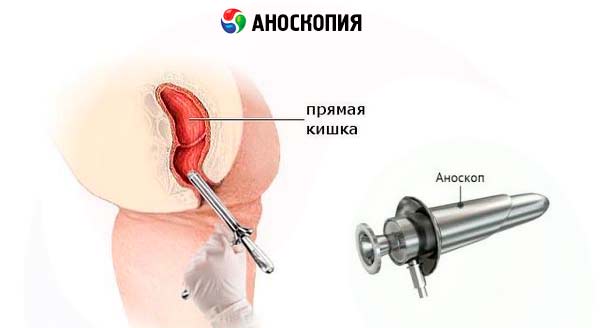
Methodology for performing anoscopy
Anoscopy can be performed without preparation. The anoscope is inserted to its full length, like a rigid sigmoidoscope, as described above, usually with the patient in the left lateral position.
The perianal area and distal part of the rectum can be examined with a 7 cm long anoscope, the rectum and sigmoid colon - with a rigid 25 cm or flexible 60 cm instrument. Sigmoidoscopy with a flexible endoscope is much more convenient for the patient and allows for photography and tissue biopsy. Only extensive practical experience allows a rigid sigmoidoscope to be advanced to the rectosigmoid region (15 cm) without causing discomfort and pain during the procedure.
Sigmoidoscopy is performed after a cleansing enema to empty the rectum. Intravenous premedication is usually not required. The patient assumes a position on the left side. After external examination and digital examination of the rectum, the device is treated with ointment and easily inserted 3-4 cm above the anal sphincter. At this point, the obturator of the hard sigmoidoscope is removed and the instrument is advanced under direct visual control.
Contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications. In patients with arrhythmias or recent myocardial ischemia, the study should be postponed until the concomitant pathology is stabilized; otherwise, cardiologist observation is necessary. Antibiotics are prescribed to patients requiring endocarditis prophylaxis.


 [
[